Correlation of monocyte/high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with progression and prognosis of type 2 diabetic nephropathy
-
摘要:目的
探讨单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值(monocyte/high density lipoprotein cholesterol,MHR)与2型糖尿病肾脏疾病(diabetic kidney disease,DKD)进展及预后的关系。
方法选取2017年1月1日至2022年12月31日在石河子大学第一附属医院肾病科确诊的269例2型DKD患者作为DKD组,同期在体检科选取269名健康体检者作为健康组,比较两组受试者MHR水平的差异。将269例DKD组患者按MHR中位数分为低水平MHR组和高水平MHR组,比较其一般资料和临床资料的差异,分析MHR水平与临床资料指标的相关性;比较两组患者终点事件的发生率,并比较不同预后DKD患者的基线肾功能及MHR水平;生存分析比较低水平MHR组和高水平MHR组患者肾脏累计生存率的差异;Cox回归分析探索DKD患者肾脏不良预后的独立危险因素;绘制受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operator characteristic curve,ROC),探索MHR对DKD不良预后的诊断效能。
结果(1)与健康组相比,DKD组患者的MHR水平[0.4918(0.3788,0.6818)×109/mmol比0.2984(0.1867,0.4112)×109/mmol]更高(P<0.05);(2)高水平MHR组患者白细胞(white blood cell,WBC)[7.70(6.40,8.70)×109/L比6.50(5.40,8.00)×109/L]、中性粒细胞(neutrophil,Ne)[4.60(3.60,5.53)×109/L比3.99(3.18,5.19)×109/L]、单核细胞(monocyte,Mono)[0.69(0.60,0.70)×109/L比0.50(0.40,0.60)×109/L]、尿白蛋白肌酐比值(urinary albumin to creatinine ratio,UACR)[1214.59(373.48,3410.02)mg/g比1050.96(180.26,3341.06)mg/g]、24 h尿蛋白定量(24 hour urine protein,24 hUP)[3.21(1.42,5.51)g比2.66(0.58,4.56)g]、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)[2.72(2.06,3.40)mmol/L比2.23(1.63,2.80)mmol/L]、血肌酐(serum creatinine,Scr)[152.10(95.20,221.60)μmol/L比126.00(92.48,186.55)μmol/L]比低水平MHR组更高;高水平MHR组淋巴细胞(lymphocyte,Lym)[1.60(1.27,2.20)×109/L比1.82(1.30,2.40)×109/L]、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(high density lipoprotein cholesterol,HDL-C)[0.94(0.83,1.07)mmol/L比1.39(1.15,1.65)mmol/L]、估算肾小球滤过率(estimated glomerular filtration rate,eGFR)[39.69(25.19,65.10)mL·min−1·(1.73 m²)−1比47.12(28.86,73.60)mL·min−1·(1.73 m²)−1]比低水平MHR组更低,高水平MHR组肾脏累计生存时间[63(39,72)月比72(46,72)月]比低水平MHR组更短(P<0.05);(3)MHR与WBC、Ne、Mono、UACR、24 hUP、Scr、LDL-C呈正相关(P<0.05),与Lym、HDL-C、eGFR、肾脏累计生存时间呈负相关(P<0.05);(4)高水平MHR组患者终点事件发生率(52.59%)比低水平MHR组(38.06%)更高(P<0.05);(5)发生终点事件的DKD患者基线MHR[0.5492(0.4030,0.7235)×109/mmol比0.4255(0.3117,0.5134)×109/mmol]、UACR[2062.65(752.80,4234.80)mg/g比608.56(88.63,1912.44)mg/g]、24 hUP[3.79(2.54,5.53)g比1.58(0.39,4.85)g]、Scr[178.40(134.00,234.23)μmol/L比100.95(74.25,152.10)μmol/L]比未发生终点事件的DKD患者更高,eGFR[33.45(23.33,46.41)mL·min−1·(1.73 m²)−1比61.59(38.57,95.98)mL·min−1·(1.73 m²)−1]比未发生终点事件的DKD患者更低(P<0.05);(6)Cox回归分析结果提示MHR是DKD不良预后的独立危险因素;(7)ROC曲线结果显示MHR的曲线下面积为0.747,灵敏度为0.820,特异度为0.605。
结论DKD患者的MHR水平较健康者高,MHR是DKD患者肾功能进展的独立危险因素,MHR对DKD患者不良预后有一定的诊断价值,但特异度不高。
-
关键词:
- 单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值 /
- 糖尿病肾脏疾病 /
- 生存分析 /
- 预后
Abstract: Objective To explore the relationship between monocyte/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (MHR) and the progression and prognosis of type 2 diabetic kidney disease (DKD).MethodsFrom January 1, 2017 to December 31, 2022, 269 type 2 DKD patients were selected as DKD group while 269 healthy medical check-ups during the same period as healthy group. And the differences in MHR levels of two groups were compared. According to median MHR, DKD group were assigned into low-level MHR and high-level MHR sub-groups. General profiles, clinical data, the incidence rate of endpoint events and cumulative renal survival were compared two groups. Cox regression analysis was performed for exploring the independent risk factors for poor renal prognosis in DKD patients and drawing receiver operator characteristic curve (ROC) for exploring the diagnostic efficacy of MHR for poor prognosis of DKD.
ResultsMHR level was higher in DKD group than that in healthy group [0.4918(0.3788, 0.6818)×109/mmol vs 0.2984(0.1867, 0.4112)×109/mmol] (P<0.05); high-level MHR group had higher levels of white blood cells (WBC) [7.70(6.40, 8.70)×109/L vs 6.50(5.40, 8.00)×109/L], neutrophils (Ne) [4.60(3.60, 5.53)×109/L vs 3.99(3.18, 5.19)×109/L] and monocyte (Mono) [0.69(0.60, 0.70)×109/L vs 0.50(0.40, 0.60)×109/L], urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR) [1214.59(373.48, 3410.02)mg/g vs 1050.96(180.26, 3341.06) mg/g], 24 h urine protein (24 hUP) [3.21(1.42, 5.51)g vs 2.66 (0.58, 4.56) g], low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) [2.72(2.06, 3.40)mmol/L vs 2.23(1.63, 2.80)mmol/L], serum creatinine (Scr) [152.10(95.20, 221.60)μmol/L vs 126.00(92.48, 186.55)μmol/L] than those in low-level MHR group; lymphocyte (Lym) [1.60(1.27, 2.20)×109/L vs 1.82(1.30, 2.40)×109/L], high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) [0.94(0.83, 1.07)mmol/L vs 1.39(1.15, 1.65)mmol/L] and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) [39.69(25.19, 65.10)mL·min−1·(1.73 m²)−1 vs 47.12(28.86, 73.60)mL·min−1·(1.73 m²)−1] were lower than those in low-level MHR group; high-level MHR group had a cumulative kidney survival time and it was shorter than that in low level MHR group [63(39, 72)month vs 72(46, 72)month] (P<0.05); MHR was correlated positively with WBC, Ne, Mono, UACR, 24h UP, Scr and LDL-C (P<0.05) and negatively with Lym, HDL-C, eGFR and cumulative renal survival time (P<0.05); the incidence of endpoint events was higher in high-level MHR group than that in low-level MHR group (52.59% vs 38.06%)(P<0.05); baseline MHR [0.5492(0.4030, 0.7235)×109/mmol vs 0.4255(0.3117, 0.5134)×109/mmol], UACR [2062.65(752.80, 4234.80)mg/g vs 608.56(88.63. 1912.44)mg/g], 24 hUP [3.79(2.54, 5.53)g vs 1.58(0.39, 4.85)g] and Scr [178.40(134.00, 234.23)μmol/L vs 100.95(74.25, 152.10)μmol/L] were higher than those in DKD patients without endpoint events; eGFR was lower than that in DKD patients without endpoint events [33.45(23.33, 46.41)mL·min−1·(1.73 m²)−1 vs 61.59(38.57, 95.98)mL·min−1·(1.73 m²)−1](P<0.05). The results of Cox regression analysis indicated that MHR was an independent risk factor for a poor prognosis of DKD; The results of ROC curve showed that the area under the curve of MHR was 0.747 with a sensitivity of 0.820 and a specificity of 0.605.
ConclusionDKD patients tend to have higher levels of MHR as compared with healthy individuals. As an independent risk for the progression of renal function in DKD patients, MHR has some diagnostic value for a poor prognosis of DKD. However, its specificity is not high.
-
糖尿病肾脏疾病(diabetic kidney disease,DKD)是一种常见的慢性肾脏病,常表现为蛋白尿排泄增加,和(或)肾小球滤过率进行性下降,疾病最终可发展为终末期肾病(end-stage renal disease,ESRD)。DKD的病理机制复杂,目前暂不完全明确,但普遍认为高血糖、高血压、氧化应激、血脂异常等均参与了DKD患者的肾功能进展过程[1-2]。单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值(monocyte/high density lipoprotein cholesterol,MHR)是近些年发现的一种与动脉粥样硬化相关的新型标志物[3-4],它同时考虑到机体的炎症反应和血脂异常状态,是众多心血管疾病的危险因素[5],当机体发生炎症反应和(或)出现血脂异常时均可引起MHR发生改变。一些研究表明,MHR与冠心病等心血管不良事件之间存在着显著的关联,MHR的升高与冠心病的发生和发展密切相关[6]。另外MHR的升高还被发现与脑卒中的发生风险增加有关,因此可以作为预测和评估脑卒中风险的一个重要指标[7]。还有研究结果显示,MHR水平增高增加了慢性肾脏病的患病风险[8],而DKD是常见的慢性肾脏病之一,目前鲜有关于MHR与DKD进展及预后的相关研究,因此本研究旨在探讨MHR与DKD进展及预后的相关性,进一步探索MHR对DKD预后判断的价值。
对象与方法
一 研究对象及分组
按纳入和排除标准选取2017年1月1日至2022年12月31日在石河子大学第一附属医院肾病科确诊的2型DKD患者281例,其中随访期间共失访12例,剩余的269例患者为DKD组,同期在体检科选取与DKD组患者年龄、性别构成大致匹配的269名健康体检者为健康组。以DKD患者的MHR中位数为界限,进一步将DKD组患者分为高水平MHR组和低水平MHR组。本研究已获得石河子大学第一附属医院伦理委员会审批(审批号:KJ2022-121-01)。
二 纳入和排除标准
1 纳入标准
DKD患者:(1)根据2021年中华医学会糖尿病学分会制定的DKD诊断标准[9],在明确糖尿病作为肾损害的病因并排除其他原因引起慢性肾脏病的情况下,至少具备下列一项者可诊断为DKD,①排除干扰因素的情况下,在3~6个月内的3次检测中至少2次尿白蛋白肌酐比值(urinary albumin to creatinine ratio,UACR)≥30 mg/g或尿白蛋白排泄率≥30 mg/24 h(≥20 μg/min);②估算肾小球滤过率(estimated glomerular filtration rate,eGFR)<60 mL·min−1·(1.73 m²)−1持续3个月以上;③肾活检符合DKD的病理改变。(2)每3个月至少随访一次。健康组体检者:(1)常规体检资料包括血尿常规、肝肾功能、心电图、胸片等结果基本正常;(2)既往无任何基础疾病,尤其是无糖尿病病史;(3)年龄及性别构成整体与DKD组患者匹配。
2 排除标准
(1)1型糖尿病;(2)缺乏人口资料及临床数据者;(3)严重的心、肝、肺器官病变者;(4)心肌梗死、脑梗死、脑出血等心脑血管疾病严重后遗症者;(5)ESRD患者或初次就诊已行肾脏替代治疗的患者;(6)血液系统疾病和恶性肿瘤者;(7)入组时3个月内有严重感染者;(8)随访期间失访者。
三 终点事件
血肌酐(serum creatinine,Scr)翻倍、eGFR相较于基线至少下降1/2、新进入ESRD、接受肾脏替代治疗(透析或者肾移植)、病死被定义为终点事件,发生终点事件被定义为肾脏不良预后。
四 随访方式
采用人工查阅患者住院或门诊病案信息、电话联系患者来院抽血复查等多种方式随访,其中电话联系患者来院抽血复查的时间间隔约1个月,随访截止时间为2023年12月31日。
五 观察指标
1 一般资料
患者性别、初次就诊时的年龄、身高、体重、体重指数(body mass index,BMI)、收缩压(systolic blood pressure,SBP)、舒张压(diastolic blood pressure,DBP)、脉压差(pulse pressure difference,PP)。
2 临床资料
白细胞(white blood cell,WBC)、中性粒细胞(neutrophil,Ne)、淋巴细胞(lymphocyte,Lym)、单核细胞(monocyte,Mono)、血红蛋白(hemoglobin,Hb)、血小板(blood platelet,PLT)、尿微量白蛋白(microalbumin,mALB)、尿肌酐(urinary creatinine,Ucr)、UACR、24 h尿蛋白定量(24 h urine protein quantification,24 hUP)、Scr、eGFR、白蛋白(albumin,ALB)、血尿酸(uric acid,UA)、尿素氮(blood urea nitrogen,BUN)、空腹血糖(fasting blood sugar,FBG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(high density lipoprotein cholesterol,HDL-C),通过Mono与HDL-C的比值得出MHR。
3 肾脏累计生存时间
通过随访,记录是否发生终点事件,若发生终点事件,则及时记录发生终点事件的时间,以此计算肾脏的累计生存时间。
六 统计学方法
计量资料符合正态分布的以$ \bar x \pm s $表示,不符正态分布的以M(Q1,Q3)表示,组间比较采用t检验或秩和检验或χ2检验;分类资料以例(%)表示,组间比较采用χ2检验。分析DKD组与健康组一般资料及MHR水平的差异;比较低水平MHR组与高水平MHR组患者一般资料和临床资料的差异,Spearman秩相关分析比较不同MHR水平组间差异有统计学意义的指标与MHR的相关关系;χ2检验比较低水平MHR组与高水平MHR组DKD患者终点事件发生率的差异,以Kaplan-Meier法进行生存分析,用Log⁃rank检验比较不同水平MHR组DKD患者肾脏累积生存率的差异;比较不同预后DKD患者基线肾功能、MHR水平;Cox回归分析探索DKD患者肾脏不良预后的独立危险因素;绘制受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operator characteristic curve,ROC),探索MHR对DKD不良预后的诊断效能。所有检验均为双侧检验,P<0.05视为差异具有统计学意义。所有数据均采用SPSS 26.0进行数据统计分析,GraphPad Prism 8.0.2进行图表绘制。
结 果
一 DKD组患者与健康组受试者一般资料及MHR的比较
DKD组患者与健康组受试者一般资料的比较中,性别构成、年龄、身高、体重、BMI差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。与健康组相比,DKD组MHR水平更高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。(表1)
表 1 DKD组患者与健康组受试者一般资料及MHR的比较Table 1. Comparison of general profiles and MHR between DKD and healthy groups项目 DKD组(n=269) 健康组(n=269) t/Z/χ2值 P值 男性[例(%)] 173(64.31) 158(58.74) 1.767 0.215 年龄(岁) 62(54,74) 58(50,70) −1.863 0.086 身高(cm) 169(159,176) 171(160,175) −0.466 0.686 体重(kg,$ \bar x\pm s $) 72.65 ± 12.90 71.52 ± 13.60 0.852 0.376 BMI(kg/m2) 25.38(23.26,27.96) 25.06(22.64,27.32) −1.266 0.262 MHR(×109/mmol) 0.4918(0.3788,0.6818) 0.2984(0.1867,0.4112) −12.475 <0.001 注:DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;MHR为单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值;BMI为体重指数;数据形式除标注外,均为M(Q1,Q3)。 二 不同水平MHR组患者一般资料的比较
DKD组患者整体MHR中位数为0.4918,其中低水平MHR组134例,高水平MHR组135例。低水平MHR组与高水平MHR组患者相比,性别构成、年龄、身高、体重、BMI、SBP、DBP、PP差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。(表2)
表 2 不同水平MHR组患者一般资料的比较Table 2. Comparison of general profiles in groups with different levels of MHR项目 低水平MHR组(n=134) 高水平MHR组(n=135) t/Z/χ2值 P值 男性[例(%)] 81(60.45) 92(68.15) 1.737 0.187 年龄(岁) 59.00(53.75,74.00) 63.00(55.00,75.00) −1.663 0.096 身高(cm) 170(160,175) 168(162,174) −0.357 0.721 体重(kg,$ \bar x \pm s $) 73.22 ± 13.20 71.91 ± 12.60 0.834 0.405 BMI(kg/m2) 25.37(23.44,28.52) 25.39(23.12,27.64) −0.873 0.383 SBP(mmHg) 150(133,166) 143(130,159) −1.808 0.071 DBP(mmHg) 80(71,90) 79(70,89) −1.296 0.195 PP(mmHg) 68(55,80) 63(55,75) −1.127 0.260 注:MHR为单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值;BMI为体重指数;SBP为收缩压;DBP为舒张压;PP为脉压差;1 mmHg=0.133 kPa;数据形式除标注外,均为M(Q1,Q3)。 三 不同水平MHR组患者临床资料的比较
与低水平MHR组相比,高水平MHR组患者WBC、Ne、Mono、UACR、24 hUP、LDL-C、Scr更高,Lym、HDL-C、eGFR更低,肾脏累计生存时间更短,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组在Hb、PLT、mALB、Ucr、ALB、BUN、UA、FBG的比较上,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。(表3)
表 3 不同水平MHR组患者临床资料的比较Table 3. Comparison of clinical data in groups with different levels of MHR指标 低水平MHR组(n=134) 高水平MHR组(n=135) t/Z/χ2值 P值 WBC(×109/L) 6.50(5.40,8.00) 7.70(6.40,8.70) −4.123 <0.001 Ne(×109/L) 3.99(3.18,5.19) 4.60(3.60,5.53) −2.254 0.024 Lym(×109/L) 1.82(1.30,2.40) 1.60(1.27,2.20) 0.398 0.039 Mono(×109/L) 0.50(0.40,0.60) 0.69(0.60,0.70) −9.208 <0.001 Hb(g/L,$ \bar x \pm s $) 113.41 ± 24.91 106.10 ± 28.74 2.228 0.227 PLT(×109/L,$ \bar x \pm s $) 237.27 ± 73.42 228.05 ± 71.56 1.043 0.298 mALB(mg/L) 611.47(142.20,1657.30) 644.04(253.49,1846.89) −0.990 0.322 Ucr(μmol/L) 5791.08(3760.80,8454.85) 5126.80(3759.00,7315.90) 1.220 0.222 UACR(mg/g) 1050.96(180.26,3341.06) 1214.59(373.48,3410.02) −0.261 0.034 24 hUP(g) 2.66(0.58,4.56) 3.21(1.42,5.51) −2.480 0.013 ALB(g/L,$ \bar x \pm s $) 34.28 ± 7.81 34.56 ± 6.29 −0.318 0.751 BUN(mmol/L) 9.13(7.02,14.84) 11.67(6.57,16.49) −1.285 0.199 Scr(μmol/L) 126.00(92.48,186.55) 152.10(95.20,221.60) −1.474 0.014 UA(μmol/L) 395.50(320.25,461.50) 373.00(325.00,459.00) −0.577 0.564 FBG(mmol/L) 6.65(5.50,7.80) 6.80(5.60,8.10) −1.462 0.078 LDL-C(mmol/L) 2.23(1.63,2.80) 2.72(2.06,3.40) −4.381 <0.001 HDL-C(mmol/L) 1.39(1.15,1.65) 0.94(0.83,1.07) −10.794 <0.001 eGFR[mL·min−1·(1.73 m2)−1] 47.12(28.86,73.60) 39.69(25.19,65.10) 1.247 0.021 生存时间(月) 72(46,72) 63(39,72) −2.360 0.018 注:MHR为单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值;WBC为白细胞;Ne为中性粒细胞;Lym为淋巴细胞;Mono为单核细胞;Hb为血红蛋白;PLT为血小板;mALB为尿微量白蛋白;Ucr为尿肌酐;UACR为尿白蛋白肌酐比值;24 hUP为24 h尿蛋白;ALB为白蛋白;BUN为尿素氮;Scr为血肌酐;UA为尿酸;FBG为空腹血糖;LDL-C为低密度脂蛋白胆固醇;HDL-C为高密度脂蛋白胆固醇;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率;数据形式除标注外,均为M(Q1,Q3)。 四 MHR与临床资料的相关性分析
Spearman秩相关分析提示MHR与WBC、Ne、Mono、UACR、24 hUP、Scr、LDL-C呈正相关,与Lym、HDL-C、eGFR、生存时间呈负相关(P<0.05)。(表4)
表 4 MHR与临床资料的相关性分析Table 4. Correlation analysis between MHR and clinical data指标 r值 P值 WBC(×109/L) 0.325 <0.001 Ne(×109/L) 0.185 0.002 Lym(×109/L) −0.142 0.020 Mono(×109/L) 0.716 <0.001 UACR(mg/g) 0.305 0.034 24 hUP(g) 0.187 0.002 Scr(μmol/L) 0.176 0.003 LDL-C(mmol/L) 0.297 <0.001 HDL-C(mmol/L) −0.651 <0.001 eGFR[mL·min−1·(1.73 m2)−1] −0.149 0.015 生存时间(月) −0.183 0.003 注:MHR为单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值;WBC为白细胞;Ne为中性粒细胞;Lym为淋巴细胞;Mono为单核细胞; UACR为尿白蛋白肌酐比值;24 hUP为24 h尿蛋白;Scr为血肌酐;LDL-C为低密度脂蛋白胆固醇;HDL-C为高密度脂蛋白胆固醇;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率。 五 不同MHR水平DKD患者的肾脏生存分析
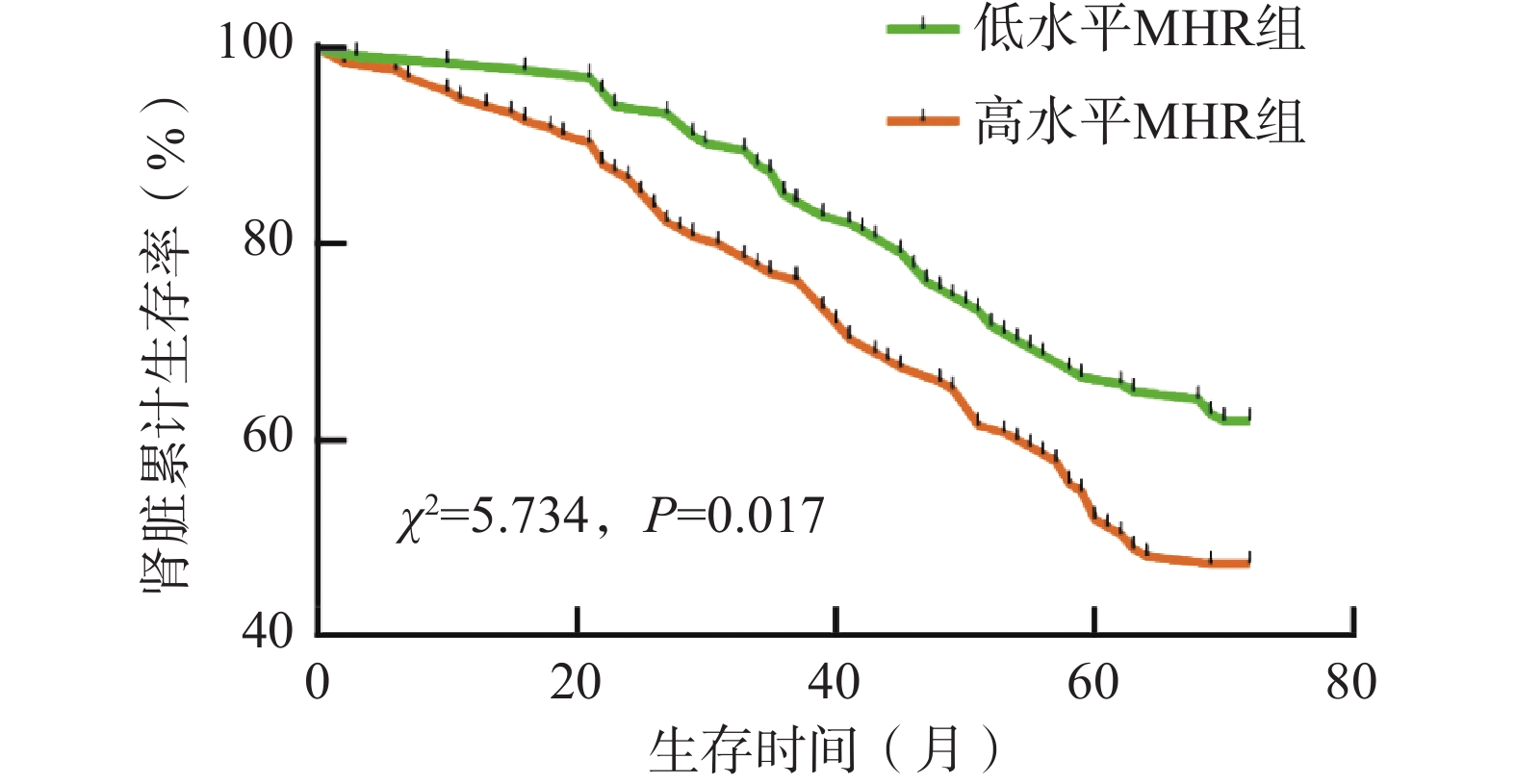
通过随访,低水平MHR组患者134例,发生终点事件51例(38.06%),高水平MHR组患者135例,发生终点事件71例(52.59%)。与低水平MHR组相比,高水平MHR组患者终点事件发生率更高,χ2=5.731,P=0.017,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。以Kaplan-Meier法进行生存分析,并绘制生存曲线,用Log⁃rank检验比较不同MHR水平DKD患者肾脏累积生存率的差异,结果为χ2=5.734,P=0.017,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。其中高水平MHR组患者肾脏中位生存时间约为63个月,低水平MHR组共随访72个月,截至随访结束时肾脏累计生存率仍未降至50%,提示低水平MHR组中位生存时间大于72个月。另外,5年肾脏累计生存率高水平MHR组为51.85%,低水平MHR组为66.42%。(图1)
六 不同预后DKD患者基线肾功能、MHR水平的比较
与未发生终点事件的DKD患者相比,发生终点事件的DKD患者基线Scr、24 hUP、UACR、MHR更高,eGFR更低,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。(表5)
表 5 不同预后DKD患者的基线肾功能、MHR水平的比较[M(Q1,Q3)]Table 5. Comparison of baseline renal function and MHR levels in DKD patients with different prognoses[M(Q1,Q3)]指标 发生终点事件(n=122) 未发生终点事件(n=147) Z值 P值 Scr(μmol/L) 178.40(134.00,234.23) 100.95(74.25,152.10) −6.990 <0.001 eGFR[mL·min−1·(1.73 m²)−1] 33.45(23.33,46.41) 61.59(38.57,95.98) −6.507 <0.001 24 hUP(g) 3.79(2.54,5.53) 1.58(0.39,4.85) −5.739 <0.001 UACR(mg/g) 2062.65(752.80,4234.80) 608.56(88.63,1912.44) −4.999 <0.001 MHR(×109/mmol) 0.5492(0.4030,0.7235) 0.4255(0.3117,0.5134) −2.772 0.006 注:MHR为单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值;DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;UACR为尿白蛋白肌酐比值;24 hUP为24 h尿蛋白定量;Scr为血肌酐;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率。 七 肾脏生存风险因素的Cox回归分析
单因素Cox回归分析结果显示WBC、Ne、Lym、Mono、Ucr、UACR、24 hUP、ALB、BUN、FBG、Scr、HDL-C、eGFR、MHR是DKD不良预后的影响因素(P<0.05),将上述指标以“向后:LR”法纳入多因素Cox回归模型,结果显示MHR、UACR、24 hUP、Scr、eGFR是DKD不良预后的独立影响因素(P<0.05),且MHR、UACR、24 hUP、Scr是DKD预后的独立危险因素(HR>1,P<0.05)。(表6)
表 6 肾脏生存风险因素的Cox回归分析Table 6. Cox regression analysis of risk factors for renal survival影响因素 单因素分析 多因素分析 P值 HR值 95%CI P值 HR值 95%CI WBC(×109/L) 0.048 1.092 (1.032~1.162) 0.182 1.124 (1.078~1.149) Ne(×109/L) 0.024 1.082 (1.049~1.233) 0.075 1.088 (1.052~1.246) Lym(×109/L) <0.001 0.548 (0.411~0.730) 0.054 0.642 (0.502~0.808) Mono(×109/L) 0.032 2.75 (1.090~6.935) 0.096 1.216 (1.103~1.324) Ucr(μmol/L) <0.001 0.926 (0.876~0.983) 0.542 0.913 (0.852~0.957) UACR(mg/g) 0.002 1.362 (1.182~1.492) 0.010 1.236 (1.135~1.332) 24 hUP(g) <0.001 1.119 (1.060~1.182) <0.001 1.143 (1.063~1.230) ALB(g/L) <0.001 0.957 (0.936~0.980) 0.069 0.962 (0.942~0.988) BUN(mmol/L) <0.001 1.071 (1.052~1.090) 0.102 1.125 (1.068~1.178) FBG(mmol/L) 0.036 1.082 (1.063~1.102) 0.062 1.075 (1.060~1.092) Scr(μmol/L) <0.001 1.007 (1.005~1.009) 0.001 1.005 (1.002~1.008) HDL-C(mmol/L) 0.034 0.602 (0.359~1.009) 0.056 0.807 (0.549~0.963) eGFR[mL·min−1·(1.73 m2)−1] <0.001 0.976 (0.968~0.984) 0.011 0.989 (0.980~0.997) MHR(×109/mmol) 0.005 2.562 (1.337~4.909) 0.036 1.186 (1.054~1.357) 注:MHR为单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值;WBC为白细胞;Ne为中性粒细胞;Lym为淋巴细胞;Mono为单核细胞; Ucr为尿肌酐;UACR为尿白蛋白肌酐比值;24 hUP为24 h尿蛋白定量;ALB为白蛋白;BUN为尿素氮;FBG为空腹血糖;Scr为血肌酐;HDL-C为高密度脂蛋白胆固醇;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率。 八 MHR预测DKD不良预后的ROC曲线
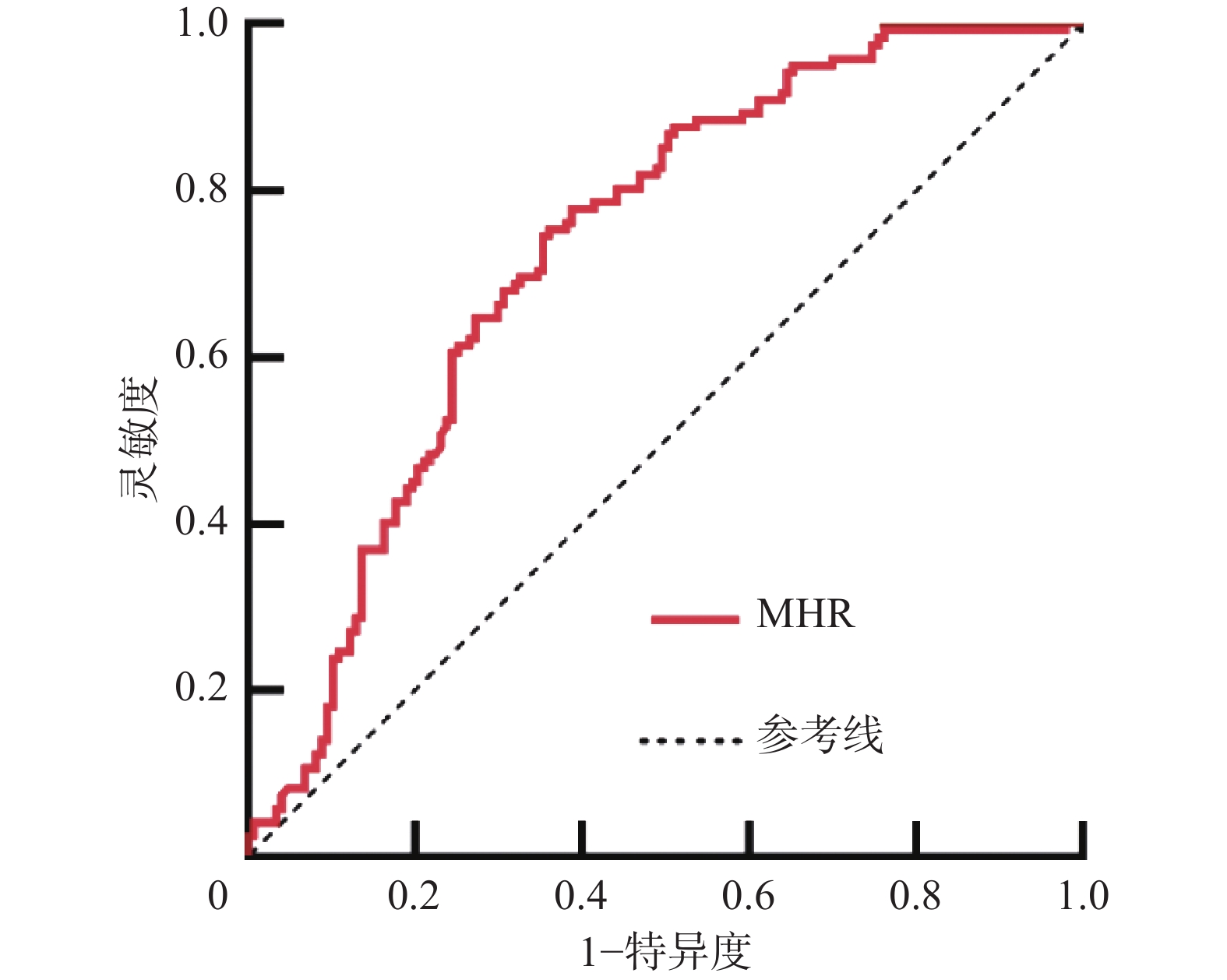
ROC曲线结果显示曲线下面积为0.747(P<0.001),95%CI为(0.689~0.806),约登指数最大值取0.425时,灵敏度为0.820,特异度为0.605。(图2)
讨 论
近些年来关于MHR的研究越来越多,MHR作为一种结合了机体的慢性炎症和血脂异常状态的新型炎症相关标志物,在预测和评估多种动脉粥样硬化疾病风险方面具有重要意义,其简便易行的检测方式使得它在临床实践中具有广泛的应用前景,为心脑血管疾病的预防和治疗提供了新的思路和方法。最新研究发现MHR与慢性肾脏病也存在一定的相关性,MHR水平与慢性肾脏病的严重程度及肾脏不良预后相关,高水平MHR可能是慢性肾脏病患者肾脏不良预后的独立预测因素[10]。
DKD是常见的慢性肾脏病,我们通过比较DKD患者与健康者的MHR水平,发现DKD患者的MHR水平显著高于健康者,这与之前的研究结果基本相符[11],提示DKD疾病的进展伴随着Mono水平的升高和(或)HDL-C水平的降低,从而导致MHR水平的升高,猜想Mono参与的炎症反应和HDL-C参与的血脂异常均参与了DKD的疾病进展。
有研究表明单核-巨噬细胞参与的免疫炎症是DKD疾病进展的一个重要环节[12-14],高糖环境可以诱导Mono趋化至肾脏,然后分化为巨噬细胞,并释放出一系列炎症因子,如白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α等,这些炎症因子能够进一步促进肾脏的炎症反应,导致肾小球和肾小管的损伤。Karthikkeyan等[15]发现DKD患者在长期较高的血糖水平刺激下,通过氧化应激使内皮细胞内产生较多的氧自由基,进一步损伤了膜蛋白酶,造成血管内皮损伤,此时Mono结合受损血管内皮上表达的黏附分子[16],之后转移至内皮下并成熟为巨噬细胞,巨噬细胞可以摄取LDL-C[17-18],然后分化为泡沫细胞,并释放促炎细胞因子,从而又吸引更多的Mono,产生炎症性胆固醇酯负荷斑块[19],形成恶性循环,进一步使局部的炎症程度和内皮功能障碍加重,从而加重了DKD患者肾功能的进展[20]。我们的研究结果与上述机制研究的结果一致,说明Mono参与的炎症反应促进了DKD的疾病进展,当DKD疾病进展时,Mono水平明显升高。
HDL-C具有逆向转运胆固醇的作用,即将胆固醇从外周组织(包括肾脏)转运回肝脏进行代谢和排泄,这一过程有助于降低肾脏中的胆固醇含量,从而减轻肾脏的脂质沉积和损伤[21]。一项前瞻性研究发现HDL-C水平的降低与DKD患者肾功能的进展关系紧密[22]。Kratzer等[23]也发现HDL-C可以作为血管内皮细胞的调节剂,抑制LDL-C对血管壁的氧化作用,从而减少LDL-C对血管内皮细胞炎症的激活。此外,HDL-C还能有效减少Mono上CD11b的表达,进而减弱Mono的促炎作用[24-25],延缓DKD患者肾功能的进展。我们的研究结果与上述机制研究的结果一致,说明HDL-C参与的血脂调节抑制了DKD的疾病进展,当DKD疾病进展时,HDL-C水平明显降低。
在反映肾脏功能的指标比较中,与低水平MHR组相比,高水平MHR组患者的UACR、24 h UP、Scr水平更高,eGFR水平更低,肾脏累计生存时间更短,且MHR与UACR、24 h UP、Scr呈正相关,与eGFR、生存时间呈负相关,提示DKD患者肾功能的进展伴随着MHR的升高,与低水平MHR组相比,高水平MHR组患者的肾脏预后更差。进一步生存分析发现,高水平MHR组患者5年肾脏累计生存率低于低水平MHR组,且高水平MHR组患者肾脏中位生存时间短于低水平MHR组,均提示高水平MHR组DKD患者的肾脏预后不如低水平MHR组DKD患者,也进一步说明MHR的升高是DKD肾脏不良预后的危险因素。
我们通过比较不同预后DKD患者基线肾功能及MHR的水平,发现与未发生终点事件的DKD患者相比,发生终点事件的DKD患者基线Scr、24 h UP、UACR、MHR水平更高,eGFR水平更低,提示较高Scr、24 h UP、UACR、MHR和较低eGFR的DKD患者更容易发生终点事件,预后更差,推测MHR、UACR、24 h UP、Scr、eGFR是影响DKD不良预后的重要因素。进一步Cox回归分析也验证了上述推测,说明MHR、UACR、24 h UP、Scr、eGFR是DKD预后的独立影响因素,其中MHR、UACR、24 h UP、Scr均为DKD不良预后的独立危险因素。
为判断MHR对DKD不良预后的诊断效能,我们进行了ROC曲线分析,结果显示曲线下面积为0.747,说明MHR可以作为DKD不良预后的诊断指标,且灵敏度较高,但其特异度稍低,这提示如果我们仅凭MHR的检测水平来判断DKD患者的预后,在一定程度上会提高假阳性率,容易对DKD患者的预后造成错误的判断。
综上所述,DKD患者肾功能的进展伴随着MHR水平的升高,当MHR升高时,在一定程度上提示了DKD患者肾功能的进展。MHR作为一种方便、经济的临床指标,可以为DKD的预后判断提供一定的参考价值,但DKD发病机制复杂,且患者自身的血糖、血脂水平等诸多因素都对MHR水平产生了一定的影响,所以仅凭MHR的检测水平仍不足以准确预测DKD患者肾功能进展的程度,因此需要我们结合UACR、24 h UP、Scr、eGFR等反映肾脏功能的其他指标来综合判断DKD患者的预后。
当然我们的研究也存在一定的局限性:(1)虽然我们的研究整体时间长达6年,但仍然有较小一部分入组时间较晚的DKD患者会因为随访时间较短,对生存时间的确定上可能存在一定的偏倚,所以需要我们后续继续对这些患者进行较长时间的随访来尽可能地降低这一部分的研究偏倚;(2)我们仅仅取MHR的中位数进行分组,以MHR的相对高低来探索MHR与DKD进展及预后的相关性,未来需要更大规模的临床研究来获得评价MHR高低的具体切点值,以期进一步为DKD的早期诊断和预后判断提供更加具体的参考价值。
-
表 1 DKD组患者与健康组受试者一般资料及MHR的比较
Table 1 Comparison of general profiles and MHR between DKD and healthy groups
项目 DKD组(n=269) 健康组(n=269) t/Z/χ2值 P值 男性[例(%)] 173(64.31) 158(58.74) 1.767 0.215 年龄(岁) 62(54,74) 58(50,70) −1.863 0.086 身高(cm) 169(159,176) 171(160,175) −0.466 0.686 体重(kg,$ \bar x\pm s $) 72.65 ± 12.90 71.52 ± 13.60 0.852 0.376 BMI(kg/m2) 25.38(23.26,27.96) 25.06(22.64,27.32) −1.266 0.262 MHR(×109/mmol) 0.4918(0.3788,0.6818) 0.2984(0.1867,0.4112) −12.475 <0.001 注:DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;MHR为单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值;BMI为体重指数;数据形式除标注外,均为M(Q1,Q3)。 表 2 不同水平MHR组患者一般资料的比较
Table 2 Comparison of general profiles in groups with different levels of MHR
项目 低水平MHR组(n=134) 高水平MHR组(n=135) t/Z/χ2值 P值 男性[例(%)] 81(60.45) 92(68.15) 1.737 0.187 年龄(岁) 59.00(53.75,74.00) 63.00(55.00,75.00) −1.663 0.096 身高(cm) 170(160,175) 168(162,174) −0.357 0.721 体重(kg,$ \bar x \pm s $) 73.22 ± 13.20 71.91 ± 12.60 0.834 0.405 BMI(kg/m2) 25.37(23.44,28.52) 25.39(23.12,27.64) −0.873 0.383 SBP(mmHg) 150(133,166) 143(130,159) −1.808 0.071 DBP(mmHg) 80(71,90) 79(70,89) −1.296 0.195 PP(mmHg) 68(55,80) 63(55,75) −1.127 0.260 注:MHR为单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值;BMI为体重指数;SBP为收缩压;DBP为舒张压;PP为脉压差;1 mmHg=0.133 kPa;数据形式除标注外,均为M(Q1,Q3)。 表 3 不同水平MHR组患者临床资料的比较
Table 3 Comparison of clinical data in groups with different levels of MHR
指标 低水平MHR组(n=134) 高水平MHR组(n=135) t/Z/χ2值 P值 WBC(×109/L) 6.50(5.40,8.00) 7.70(6.40,8.70) −4.123 <0.001 Ne(×109/L) 3.99(3.18,5.19) 4.60(3.60,5.53) −2.254 0.024 Lym(×109/L) 1.82(1.30,2.40) 1.60(1.27,2.20) 0.398 0.039 Mono(×109/L) 0.50(0.40,0.60) 0.69(0.60,0.70) −9.208 <0.001 Hb(g/L,$ \bar x \pm s $) 113.41 ± 24.91 106.10 ± 28.74 2.228 0.227 PLT(×109/L,$ \bar x \pm s $) 237.27 ± 73.42 228.05 ± 71.56 1.043 0.298 mALB(mg/L) 611.47(142.20,1657.30) 644.04(253.49,1846.89) −0.990 0.322 Ucr(μmol/L) 5791.08(3760.80,8454.85) 5126.80(3759.00,7315.90) 1.220 0.222 UACR(mg/g) 1050.96(180.26,3341.06) 1214.59(373.48,3410.02) −0.261 0.034 24 hUP(g) 2.66(0.58,4.56) 3.21(1.42,5.51) −2.480 0.013 ALB(g/L,$ \bar x \pm s $) 34.28 ± 7.81 34.56 ± 6.29 −0.318 0.751 BUN(mmol/L) 9.13(7.02,14.84) 11.67(6.57,16.49) −1.285 0.199 Scr(μmol/L) 126.00(92.48,186.55) 152.10(95.20,221.60) −1.474 0.014 UA(μmol/L) 395.50(320.25,461.50) 373.00(325.00,459.00) −0.577 0.564 FBG(mmol/L) 6.65(5.50,7.80) 6.80(5.60,8.10) −1.462 0.078 LDL-C(mmol/L) 2.23(1.63,2.80) 2.72(2.06,3.40) −4.381 <0.001 HDL-C(mmol/L) 1.39(1.15,1.65) 0.94(0.83,1.07) −10.794 <0.001 eGFR[mL·min−1·(1.73 m2)−1] 47.12(28.86,73.60) 39.69(25.19,65.10) 1.247 0.021 生存时间(月) 72(46,72) 63(39,72) −2.360 0.018 注:MHR为单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值;WBC为白细胞;Ne为中性粒细胞;Lym为淋巴细胞;Mono为单核细胞;Hb为血红蛋白;PLT为血小板;mALB为尿微量白蛋白;Ucr为尿肌酐;UACR为尿白蛋白肌酐比值;24 hUP为24 h尿蛋白;ALB为白蛋白;BUN为尿素氮;Scr为血肌酐;UA为尿酸;FBG为空腹血糖;LDL-C为低密度脂蛋白胆固醇;HDL-C为高密度脂蛋白胆固醇;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率;数据形式除标注外,均为M(Q1,Q3)。 表 4 MHR与临床资料的相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis between MHR and clinical data
指标 r值 P值 WBC(×109/L) 0.325 <0.001 Ne(×109/L) 0.185 0.002 Lym(×109/L) −0.142 0.020 Mono(×109/L) 0.716 <0.001 UACR(mg/g) 0.305 0.034 24 hUP(g) 0.187 0.002 Scr(μmol/L) 0.176 0.003 LDL-C(mmol/L) 0.297 <0.001 HDL-C(mmol/L) −0.651 <0.001 eGFR[mL·min−1·(1.73 m2)−1] −0.149 0.015 生存时间(月) −0.183 0.003 注:MHR为单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值;WBC为白细胞;Ne为中性粒细胞;Lym为淋巴细胞;Mono为单核细胞; UACR为尿白蛋白肌酐比值;24 hUP为24 h尿蛋白;Scr为血肌酐;LDL-C为低密度脂蛋白胆固醇;HDL-C为高密度脂蛋白胆固醇;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率。 表 5 不同预后DKD患者的基线肾功能、MHR水平的比较[M(Q1,Q3)]
Table 5 Comparison of baseline renal function and MHR levels in DKD patients with different prognoses[M(Q1,Q3)]
指标 发生终点事件(n=122) 未发生终点事件(n=147) Z值 P值 Scr(μmol/L) 178.40(134.00,234.23) 100.95(74.25,152.10) −6.990 <0.001 eGFR[mL·min−1·(1.73 m²)−1] 33.45(23.33,46.41) 61.59(38.57,95.98) −6.507 <0.001 24 hUP(g) 3.79(2.54,5.53) 1.58(0.39,4.85) −5.739 <0.001 UACR(mg/g) 2062.65(752.80,4234.80) 608.56(88.63,1912.44) −4.999 <0.001 MHR(×109/mmol) 0.5492(0.4030,0.7235) 0.4255(0.3117,0.5134) −2.772 0.006 注:MHR为单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值;DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;UACR为尿白蛋白肌酐比值;24 hUP为24 h尿蛋白定量;Scr为血肌酐;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率。 表 6 肾脏生存风险因素的Cox回归分析
Table 6 Cox regression analysis of risk factors for renal survival
影响因素 单因素分析 多因素分析 P值 HR值 95%CI P值 HR值 95%CI WBC(×109/L) 0.048 1.092 (1.032~1.162) 0.182 1.124 (1.078~1.149) Ne(×109/L) 0.024 1.082 (1.049~1.233) 0.075 1.088 (1.052~1.246) Lym(×109/L) <0.001 0.548 (0.411~0.730) 0.054 0.642 (0.502~0.808) Mono(×109/L) 0.032 2.75 (1.090~6.935) 0.096 1.216 (1.103~1.324) Ucr(μmol/L) <0.001 0.926 (0.876~0.983) 0.542 0.913 (0.852~0.957) UACR(mg/g) 0.002 1.362 (1.182~1.492) 0.010 1.236 (1.135~1.332) 24 hUP(g) <0.001 1.119 (1.060~1.182) <0.001 1.143 (1.063~1.230) ALB(g/L) <0.001 0.957 (0.936~0.980) 0.069 0.962 (0.942~0.988) BUN(mmol/L) <0.001 1.071 (1.052~1.090) 0.102 1.125 (1.068~1.178) FBG(mmol/L) 0.036 1.082 (1.063~1.102) 0.062 1.075 (1.060~1.092) Scr(μmol/L) <0.001 1.007 (1.005~1.009) 0.001 1.005 (1.002~1.008) HDL-C(mmol/L) 0.034 0.602 (0.359~1.009) 0.056 0.807 (0.549~0.963) eGFR[mL·min−1·(1.73 m2)−1] <0.001 0.976 (0.968~0.984) 0.011 0.989 (0.980~0.997) MHR(×109/mmol) 0.005 2.562 (1.337~4.909) 0.036 1.186 (1.054~1.357) 注:MHR为单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值;WBC为白细胞;Ne为中性粒细胞;Lym为淋巴细胞;Mono为单核细胞; Ucr为尿肌酐;UACR为尿白蛋白肌酐比值;24 hUP为24 h尿蛋白定量;ALB为白蛋白;BUN为尿素氮;FBG为空腹血糖;Scr为血肌酐;HDL-C为高密度脂蛋白胆固醇;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率。 -
[1] Pelle MC, Provenzano M, Busutti M, et al. Up-date on diabetic nephropathy[J]. Life,2022,12(8):1202. DOI: 10.3390/life12081202.
[2] Samsu N. Diabetic nephropathy: challenges in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment[J]. Biomed Res Int,2021,2021:1497449. DOI: 10.1155/2021/1497449.
[3] Acikgoz N, Kurtoğlu E, Yagmur J, et al. Elevated monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and endothelial dysfunction in behçet disease[J]. Angiology,2018,69(1):65-70. DOI: 10.1177/0003319717704748.
[4] Canpolat U, Çetin EH, Cetin S, et al. Association of monocyte-to-HDL cholesterol ratio with slow coronary flow is linked to systemic inflammation[J]. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost,2016,22(5):476-482. DOI: 10.1177/1076029615594002.
[5] Zhan XJ, Pan D, Wei X, et al. Monocyte to high-density lipoprotein ratio and cardiovascular events in patients on peritoneal dialysis[J]. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis,2020,30(7):1130-1136. DOI: 10.1016/j.numecd.2020.03.011.
[6] 余嘉清, 韩敏, 朱兵, 等. 单核细胞与高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值在心肌病发生和发展过程中的机制及研究进展[J]. 中国临床保健杂志,2021,24(5):715-720.DOI: 10.3969/J.issn.1672-6790.2021.05.031. Yu JQ, Han M, Zhu B, et al. The mechanism and research progress of the ratio of monocyte to high density lipoprotein cholesterol in the occurrence and development of cardiomyopathy[J]. Chin J Clin Healthc,2021,24(5):715-720. DOI: 10.3969/J.issn.1672-6790.2021.05.031.
[7] 郭星, 许莉莉, 何洪真, 等. 单核细胞高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值与缺血性脑卒中进展和预后的研究进展[J]. 国际神经病学神经外科学杂志,2022,49(1):87-90.DOI: 10.16636/j.cnki.jinn.1673-2642.2022.01.018. Guo X, Xu LL, He HZ, et al. Research progress of monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and its association with ischemic stroke progression and prognosis[J]. J Int Neurol Neurosurg,2022,49(1):87-90. DOI: 10.16636/j.cnki.jinn.1673-2642.2022.01.018.
[8] Li XW, Cui L, Xu HY. Association between systemic inflammation response index and chronic kidney disease: a population-based study[J/OL]. Front Endocrinol,2024,15:1329256. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1329256.
[9] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会微血管并发症学组. 中国糖尿病肾脏病防治指南(2021年版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2021,13(8):762-784.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20210706-00369. Microvascular Complications Group of the Diabetes Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of diabetic kidney disease in China (2021 edition)[J]. Chin J Diabetes Mellit,2021,13(8):762-784. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20210706-00369.
[10] 吴美豪, 曹慧霞, 王丽姣, 等. 单核细胞/高密度脂蛋白比值与慢性肾脏病疾病严重程度及预后的关系[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志,2021,37(7):567-575.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441217-20210202-00086. Wu MH, Cao HX, Wang LJ, et al. Relationship between monocyte/high-density lipoprotein ratio and severity and prognosis of chronic kidney disease[J]. Chin J Nephrol,2021,37(7):567-575. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441217-20210202-00086.
[11] 黄文娟, 万辛. 单核细胞与高密度脂蛋白比值与糖尿病肾脏疾病的相关性研究[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志,2019,19(12):891-894.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.2019.12.006. Huang WJ, Wan X. The correlation between the monocyte to HDL ratio and diabetic kidney disease[J]. J Clin Nephrol,2019,19(12):891-894. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.2019.12.006.
[12] Jung SW, Moon JY. The role of inflammation in diabetic kidney disease[J]. Korean J Intern Med,2021,36(4):753-766. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2021.174.
[13] Kong LY, Andrikopoulos S, MacIsaac RJ, et al. Role of the adaptive immune system in diabetic kidney disease[J]. J Diabetes Investig,2022,13(2):213-226. DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13725.
[14] Wan SF, Wan SK, Jiao XJ, et al. Advances in understanding the innate immune-associated diabetic kidney disease[J/OL]. FASEB J,2021,35(2):e21367. DOI: 10.1096/fj.202002334R.
[15] Karthikkeyan G, Nareshkumar RN, Aberami S, et al. Hyperglycemia induced early growth response-1 regulates vascular dysfunction in human retinal endothelial cells[J]. Microvasc Res,2018,117:37-43. DOI: 10.1016/j.mvr.2018.01.002.
[16] Tani S, Matsumoto M, Anazawa T, et al. Development of a model for prediction of coronary atherosclerotic regression: evaluation of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level and peripheral blood monocyte count[J]. Heart Vessels,2012,27(2):143-150. DOI: 10.1007/s00380-011-0130-8.
[17] Açıkgöz SK, Açıkgöz E, Şensoy B, et al. Monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is predictive of in-hospital and five-year mortality in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction[J]. Cardiol J,2016,23(5):505-512. DOI: 10.5603/CJ.a2016.0026.
[18] Kundi H, Kiziltunc E, Cetin M, et al. Association of monocyte/HDL-C ratio with SYNTAX scores in patients with stable coronary artery disease[J]. Herz,2016,41(6):523-529. DOI: 10.1007/s00059-015-4393-1.
[19] Zadeh JK, Zhutdieva MB, Laspas P, et al. Apolipoprotein E deficiency causes endothelial dysfunction in the mouse retina[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev,2019,2019:5181429. DOI: 10.1155/2019/5181429.
[20] Galkina E, Ley K. Leukocyte recruitment and vascular injury in diabetic nephropathy[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol,2006,17(2):368-377. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2005080859.
[21] Zuzda K, Grycuk W, Małyszko J, et al. Kidney and lipids: novel potential therapeutic targets for dyslipidemia in kidney disease?[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets,2022,26(11):995-1009. DOI: 10.1080/14728222.2022.2161887.
[22] Morton J, Zoungas S, Li Q, et al. Low HDL cholesterol and the risk of diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy: results of the ADVANCE study[J]. Diabetes Care,2012,35(11):2201-2206. DOI: 10.2337/dc12-0306.
[23] Kratzer A, Giral H, Landmesser U. High-density lipoproteins as modulators of endothelial cell functions: alterations in patients with coronary artery disease[J]. Cardiovasc Res,2014,103(3):350-361. DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvu139.
[24] Hui N, Barter PJ, Ong KL, et al. Altered HDL metabolism in metabolic disorders: insights into the therapeutic potential of HDL[J]. Clin Sci,2019,133(21):2221-2235. DOI: 10.1042/CS20190873.
[25] van Oostrom AJ, van Wijk JP, Sijmonsma TP, et al. Increased expression of activation markers on monocytes and neutrophils in type 2 diabetes[J]. Neth J Med,2004,62(9):320-325. DOI: 10.4065/79.10.1341-a.







 下载:
下载:

.png)