Value of serum endothelial nitric oxide synthase and Omentin-1 levels for predicting the occurrence of diabetes nephropathy in type 2 diabetes patients
-
摘要:目的
分析2型糖尿病患者血清内皮型一氧化氮合酶(endothelial nitric oxide synthase,eNOS)、网膜素1(Omentin-1)水平对糖尿病肾脏疾病(diabetic kidney disease,DKD)发生的预测价值。
方法选取2020年5月至2023年2月石家庄市第二医院收治的2型DKD患者124例作为DKD组、单纯2型糖尿病患者125例作为对照组。收集所有患者的临床指标;酶联免疫吸附法检测患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1水平;Pearson法分析DKD患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1和临床指标的相关性;多因素Logistic回归模型分析影响2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的危险因素;受试者工作特征曲线分析2型糖尿病患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1水平对DKD发生的预测价值。
结果与对照组比较,DKD组患者血清总胆固醇[(4.75 ± 0.91)mmol/L比(4.48 ± 0.96)mmol/L]、糖化血红蛋白[(9.32 ± 1.25)%比(8.56 ± 1.23)%]、24 h尿蛋白定量[(2.78 ± 0.31)g比(0.15 ± 0.02)g]、尿微量白蛋白(urinary microalbumin,mAlb)[(273.12 ± 20.41)mg/L比(23.08 ± 3.35)mg/L]、血肌酐(serum creatinine,Scr)[(209.53 ± 22.59)μmol/L比(73.52 ± 9.21)μmol/L]水平显著升高,估算肾小球滤过率(estimated glomerular filtration rate,eGFR)[(72.52 ± 13.51)mL·min−1·(1.73 m2)−1比(107.34 ± 10.27)mL·min−1·(1.73 m2)−1]、血清eNOS[(24.48 ± 3.37)U/L比(33.82 ± 4.52)U/L]、Omentin-1[(28.75 ± 4.42)μg/L比(43.63 ± 6.78)μg/L]水平显著降低(P<0.05);DKD患者血清eNOS与Omentin-1水平呈正相关(r = 0.674,P<0.05);血清eNOS、Omentin-1与24 h尿蛋白定量、mAlb、Scr呈负相关(r = −0.456、−0.551、−0.503、−0.527、−0.497、−0.495,P<0.05),与eGFR呈正相关(r = 0.523、0.602,P<0.05);24 h尿蛋白定量、mAlb、Scr是影响2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的危险因素(P<0.05),eGFR、eNOS、Omentin-1是影响2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的保护因素(P<0.05);血清eNOS、Omentin-1两者联合预测2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC)为0.942,分别高于血清eNOS(AUC = 0.882)、Omentin-1(AUC = 0.862)各自单独预测2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的AUC(P<0.05)。
结论DKD患者血清eNOS与Omentin-1水平均呈低表达,二者联合检测对2型糖尿病患者发生DKD有一定预测价值。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the predictive value of serum levels of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and Omentin-1 for the occurrence of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.
MethodsFrom May 2020 to February 2023, 124 hospitalized patients with type 2 DKD were selected as DKD group and 125 patients with simple type 2 diabetes as control group. Clinical parameters of all patients were collected. Serum levels of eNOS and Omentin-1 were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Pearson’s method was utilized for examining the correlation between serum eNOS, Omentin-1 and clinical parameters. Multivariate Logistic regression model was employed for examining the risk factors of DKD occurrence in T2DM. The predictive value of serum levels of eNOS and Omentin-1 for the occurrence of DKD was examined by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
ResultsAs compared with control group, serum levels of total cholesterol [(4.75±0.91) mmol/L vs (4.48±0.96) mmol/L], glycosylated hemoglobin [(9.32±1.25)% vs (8.56±1.23)%], 24 h urinary protein quantity [(2.78±0.31) g vs (0.15±0.02) g], urinary microalbumin (mAlb) [(273.12±20.41) mg/L vs (23.08±3.35) mg/L] and serum creatinine (Scr) [(209.53±22.59) μmol/L vs (73.52±9.21) μmol/L] spiked markedly in DKD group. And the levels of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) [(72.52±13.51) mL·min−1·(1.73 m2)−1 vs (107.34±10.27) mL·min−1·(1.73 m2)−1], serum eNOS [(24.48±3.37) U/L vs (33.82±4.52) U/L] and Omentin-1 [ (28.75±4.42) μg/L vs (43.63±6.78) μg/L] rose sharply (P<0.05). A positive correlation existed between serum eNOS and Omentin-1 level (r=0.674, P<0.05). Serum levels of eNOS and Omentin-1 were correlated negatively with 24 h urinary protein quantity, mAlb and Scr (r=−0.456, −0.551, −0.503, −0.527, −0.497, −0.495, P<0.05) and yet positively with eGFR (r=0.523, 0.602, P<0.05). 24 h urinary protein quantity, mAlb and Scr were risk factors for DKD occurrence in T2DM (P<0.05) while eGFR, eNOS and Omentin-1 were protective factors for DKD occurrence in T2DM (P<0.05). The area under curve (AUC) of serum eNOS plus Omentin-1 in predicting DKD occurrence in T2DM was 0.942. It was higher than that of serum eNOS (AUC=0.882) and Omentin-1 (AUC=0.862) separately predicting DKD occurrence in T2DM patients (P<0.05).
ConclusionsSerum levels of eNOS and Omentin-1 are both low and a combined detection of both has some predictive values for the occurrence of DKD in T2DM patients.
-
糖尿病肾脏疾病(diabetic kidney disease,DKD)是糖尿病患者的常见并发症,累及10%~30%的糖尿病患者,若不及时治疗可能引起慢性肾衰竭甚至死亡,其病死率占糖尿病患者的60%~70%[1]。因此DKD的早期诊断和预后评估对DKD的治疗具有重要意义。一氧化氮合酶(nitric oxide synthase,NOS)是一种同工酶,内皮型一氧化氮合酶(endothelial nitric oxide synthase,eNOS)是其中一种,可产生一氧化氮,在内皮细胞的稳定性和血管疾病的发病中具有重要作用[2]。景梦怡等[3]研究表明,DKD小鼠模型中,小鼠肾组织中eNOS信使RNA和蛋白表达水平明显下调。网膜素1(Omentin-1)是一种脂肪细胞因子,与胰岛素抵抗、糖脂代谢紊乱、炎症反应等密切相关,也与DKD的发生发展有关[4]。研究表明,妊娠糖尿病患者血清Omentin-1水平降低与胰岛素抵抗密切相关,Omentin-1低表达提示糖代谢紊乱及胰岛素抵抗[5]。目前尚未见eNOS、Omentin-1同时在DKD患者中表达情况的研究报道。本研究检测eNOS、Omentin-1在DKD患者血清中的表达情况,探讨二者与DKD患者肾损害的关系,现报道如下。
对象与方法
一 研究对象
选取2020年5月至2023年2月石家庄市第二医院收治的124例2型DKD患者作为DKD组,其中男68例,女56例,年龄(53.50 ± 8.50)岁;另选取同期125例单纯2型糖尿病患者作为对照组,其中男60例,女65例,年龄(52.80 ± 8.70)岁。纳入标准:(1)DKD组患者符合DKD诊断标准[6],且所有DKD患者均经肾活检确诊,对照组患者符合2型糖尿病诊断标准[7];(2)年龄≥18岁;(3)患者病历资料完整。排除标准:(1)1型糖尿病患者;(2)合并膜性肾病、紫癜性肾病、免疫球蛋白A肾病等其他肾脏疾病者;(3)使用过糖皮质激素或免疫调节药物者。本研究获得石家庄市第二医院伦理委员会批准(批件编号:临床伦审2020-005号),所有患者均签署知情同意书。
二 主要试剂与仪器
人eNOS、Omentin-1酶联免疫吸附(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)测定试剂盒(批号分别为FT-P3273、FT-P4617)购自武汉益普生物科技有限公司;酶标仪(型号:EnVision)购自焦作云之羽生物科技有限公司。
三 研究方法
1 临床指标收集
收集所有患者入院就诊时年龄、性别、体重指数(body mass index,BMI)、收缩压(systolic blood pressure,SBP)、舒张压(diastolic blood pressure,DBP)、空腹血糖(fasting blood glucose,FPG)、糖化血红蛋白(glycosylated hemoglobin,HbA1c)、血肌酐(serum creatinine,Scr)、总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)、24 h尿蛋白定量、尿微量白蛋白(urinary microalbumin,mAlb),并根据Scr水平计算估算肾小球滤过率(estimated glomerular filtration rate,eGFR)[8]水平。
2 血清eNOS、Omentin-1水平检测
采集所有患者就诊时清晨空腹静脉血5 mL,静置30 min后,5700 r/min,离心半径10 cm,离心20 min后收集血清,采用ELISA法检测血清eNOS、Omentin-1水平。
四 统计学方法
采用SPSS 24.0软件处理数据,计量资料(均符合正态分布)以$ \bar x $ ± $ s $表示,两组间比较采用t检验;计数资料采用例数表示,两组间比较采用χ2检验;Pearson法分析DKD患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1和临床指标的相关性;多因素Logistic回归模型分析影响2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的危险因素;受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线分析2型糖尿病患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1水平对DKD发生的预测价值,曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC)比较行Z检验;P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
结 果
一 对照组和DKD组患者临床指标比较
对照组与DKD组患者年龄、性别、BMI、SBP、DBP、FPG水平差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。与对照组比较,DKD组患者血清TC、HbA1c、24 h尿蛋白定量、mAlb、Scr水平显著升高,eGFR水平显著降低(P<0.05)。(表1)
表 1 对照组和DKD组患者临床指标比较Table 1. Comparison of clinical parameters between control and DKD groups指标 对照组(n=125) DKD组(n=124) χ2/t值 P值 年龄(岁,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 52.80 ± 8.70 53.50 ± 8.50 0.642 0.521 男性(例) 60 68 1.165 0.280 BMI(kg/m2,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 26.24 ± 3.36 25.81 ± 3.15 1.042 0.299 SBP(mmHg,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 131.21 ± 9.31 129.84 ± 8.17 1.234 0.218 DBP(mmHg,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 89.43 ± 12.21 87.45 ± 11.32 1.327 0.186 TC(mmol/L,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 4.48 ± 0.96 4.75 ± 0.91 2.277 0.024 FPG(mmol/L,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 8.48 ± 1.57 8.51 ± 1.54 0.152 0.879 HbA1c(%,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 8.56 ± 1.23 9.32 ± 1.25 4.836 <0.001 24 h尿蛋白定量(g,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 0.15 ± 0.02 2.78 ± 0.31 94.656 <0.001 mAlb(mg/L,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 23.08 ± 3.35 273.12 ± 20.41 135.148 <0.001 Scr(μmol/L,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 73.52 ± 9.21 209.53 ± 22.59 62.298 <0.001 eGFR[mL·min−1·(1.73 m2)−1,$\bar{x} \pm s $] 107.34 ± 10.27 72.52 ± 13.51 22.906 <0.001 注:DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;BMI为体重指数;SBP为收缩压;DBP为舒张压;TC为总胆固醇;FPG为空腹血糖;HbA1c为糖化血红蛋白;mAlb为尿微量白蛋白;Scr为血肌酐;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率;1 mmHg=0.133 kPa。 二 对照组和DKD组患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1水平比较
与对照组比较,DKD组患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1水平显著降低(P<0.05)。(表2)
表 2 对照组和DKD组患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1水平比较($\bar{x} \pm s$)Table 2. Comparison of serum levels of eNOS and Omentin-1 between control and DKD groups($\bar{x} \pm s $)组别 例数 eNOS(U/L) Omentin-1(μg/L) 对照组 125 33.82 ± 4.52 43.63 ± 6.78 DKD组 124 24.48 ± 3.37 28.75 ± 4.42 t值 - 18.474 20.497 P值 - <0.001 <0.001 注:DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;eNOS为内皮型一氧化氮合酶;Omentin-1为网膜素1。 三 DKD患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1和临床指标的相关性分析
Pearson法分析显示,DKD患者血清eNOS与Omentin-1水平呈正相关(P<0.05);血清eNOS、Omentin-1与24 h尿蛋白定量、mAlb、Scr呈负相关(P<0.05),与eGFR呈正相关(P<0.05),与血清TC、HbA1c无明显相关性(P>0.05)。(表3)
表 3 DKD患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1和临床指标的相关性分析Table 3. Correlation analysis of serum levels of eNOS and Omentin-1 and clinical parameters in DKD patients指标 eNOS Omentin-1 r值 P值 r值 P值 TC −0.152 0.141 −0.113 0.136 HbA1c −0.085 0.203 −0.173 0.105 24 h尿蛋白定量 −0.456 <0.001 −0.551 <0.001 mAlb −0.503 <0.001 −0.527 <0.001 Scr −0.497 <0.001 −0.495 <0.001 eGFR 0.523 <0.001 0.602 <0.001 Omentin-1 0.674 <0.001 - - 注:DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;eNOS为内皮型一氧化氮合酶;Omentin-1为网膜素1;TC为总胆固醇;HbA1c为糖化血红蛋白;mAlb为尿微量白蛋白;Scr为血肌酐;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率。 四 影响2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的多因素分析
以2型糖尿病患者发生DKD为因变量,以TC、HbA1c、24 h尿蛋白定量、mAlb、Scr、eGFR、eNOS、Omentin-1的实测值为自变量进行多因素Logistic回归分析,结果显示,24 h尿蛋白定量、mAlb、Scr是影响2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的危险因素(P<0.05),eGFR、eNOS、Omentin-1是影响2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的保护因素(P<0.05)。(表4)
表 4 影响2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的多因素Logistic回归分析Table 4. Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of DKD occurrence in T2DM patients自变量 B值 SE值 Wald值 OR值 95% CI P值 TC 0.054 0.273 0.039 1.056 0.618~1.803 0.841 HbA1c 0.450 0.297 2.300 1.569 0.877~2.808 0.129 24 h尿蛋白定量 0.950 0.305 9.712 2.587 1.423~4.703 0.001 mAlb 1.104 0.413 7.140 3.015 1.342~6.774 0.007 Scr 0.976 0.324 9.075 2.654 1.406~5.008 0.002 eGFR −0.247 0.105 5.541 0.781 0.635~0.959 0.019 eNOS −0.365 0.117 9.747 0.694 0.552~0.873 0.002 Omentin-1 −0.346 0.124 7.818 0.707 0.554~0.901 0.005 注:DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;TC为总胆固醇;HbA1c为糖化血红蛋白;mAlb为尿微量白蛋白;Scr为血肌酐;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率;eNOS为内皮型一氧化氮合酶;Omentin-1为网膜素1。 五 2型糖尿病患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1水平对DKD发生的预测价值
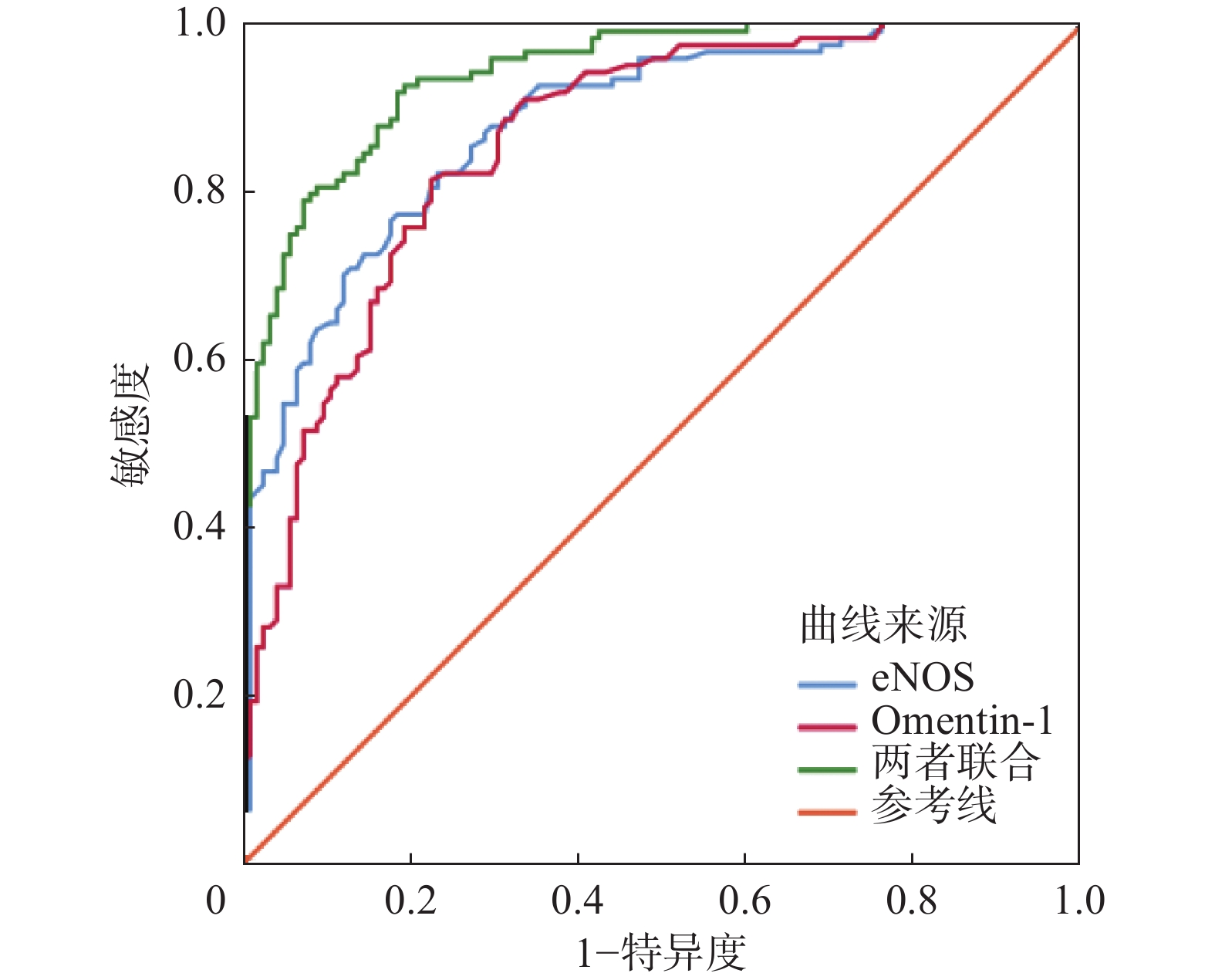
ROC曲线发现,血清eNOS、Omentin-1二者联合预测2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的AUC分别高于血清eNOS、Omentin-1各自单独预测2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的AUC(Z=2.427,P=0.015;Z=3.017,P=0.003)。(表5、图1)
表 5 2型糖尿病患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1水平对DKD发生的预测价值Table 5. Predictive value of serum levels of eNOS and Omentin-1 for DKD occurrence in T2DM patients指标 AUC 95%CI 截断值 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 约登指数 eNOS(U/L) 0.882 0.835~0.919 29.60 77.42 82.40 0.598 Omentin-1(μg/L) 0.862 0.812~0.902 36.93 81.45 77.60 0.591 二者联合 0.942 0.906~0.968 - 92.74 80.80 0.735 注:eNOS为内皮型一氧化氮合酶;Omentin-1为网膜素1;DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;AUC为曲线下面积。 讨 论
DKD患病率呈上升趋势,尤其在老年人中的发病率明显升高,DKD能导致终末期肾病,威胁患者健康。因此,早期诊断、及时治疗DKD具有重要意义[9]。
NOS是一种同工酶,有3种亚型,eNOS是其中一种亚型。eNOS可在Ca2+及钙调蛋白作用下产生一氧化氮,在抗炎、抗血栓方面可发挥重要作用[10]。胡玲等[11]研究表明,eNOS基因突变与DKD的发生密切相关,eNOS基因G894T多态性可明显增加2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的风险。研究显示,尼古丁诱导的大鼠急性肾损伤模型中,肾小球硬化和肾小管细胞变性明显,且eNOS水平降低,非诺贝特诱导的eNOS上调表达可改善尼古丁诱导的急性肾损伤[12]。以上研究表明,eNOS与肾损伤等疾病密切相关。本研究结果显示,DKD患者血清eNOS水平较单纯2型糖尿病患者显著降低,提示eNOS参与DKD发生,分析原因为DKD属于糖尿病微血管病变,存在内皮功能障碍,eNOS水平降低,而eNOS具有内皮功能保护效应,可影响血管舒张,加强血流供应,使得内皮细胞黏附性降低,其表达缺失可以造成内皮损伤,增进eNOS二聚体活性是治疗DKD的一个新方向[13]。
Omentin-1是一种主要由基质血管细胞分泌的重要脂肪因子,可降低炎症,改善氧化应激和内皮功能,参与调节炎症反应、糖脂代谢,与糖尿病、肥胖、癌症、心血管疾病密切相关[14]。Song等[15]研究显示,给予2型糖尿病小鼠Omentin-1治疗,可减少促炎细胞因子的产生,并改善肾组织中的氧化应激水平,改善小鼠的肾功能。徐静[16]研究显示,2型糖尿病合并外周动脉疾病患者血清Omentin-1水平降低,Omentin-1可影响2型糖尿病患者外周动脉疾病的发生。本研究结果显示,DKD患者血清Omentin-1水平较单纯2型糖尿病患者显著降低,提示Omentin-1与DKD的发生有关,可能原因是DKD患者内皮细胞炎症和氧化应激增强,抑制了Omentin-1的合成,使得Omentin-1水平降低。
本研究显示,与单纯2型糖尿病患者比较,DKD患者血清TC、HbA1c、24 h尿蛋白定量、mAlb、Scr水平显著升高,eGFR水平显著降低,提示DKD患者存在脂代谢异常和肾损伤。相关性分析显示,DKD患者血清eNOS与Omentin-1水平呈正相关,血清eNOS、Omentin-1水平与24 h尿蛋白定量、mAlb、Scr呈负相关,与eGFR呈正相关,进一步提示eNOS和Omentin-1可能存在相互作用的关系,且二者均与肾功能损伤有着密切联系。Logistic多因素分析显示,24 h尿蛋白定量、mAlb、Scr是影响2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的危险因素,eGFR、eNOS、Omentin-1是影响2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的保护因素,提示eNOS、Omentin-1水平降低糖尿病患者发生DKD的风险增加,升高eNOS、Omentin-1水平可能是治疗DKD的新方向。ROC曲线分析显示,血清eNOS、Omentin-1联合预测2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的AUC为0.942,敏感度为92.74%,特异度为80.80%,且联合预测效能高于单独检测,提示血清eNOS、Omentin-1对2型糖尿病患者发生DKD有一定的预测价值,在临床上可作为诊断DKD的辅助指标。
综上所述,DKD患者血清eNOS与Omentin-1水平均呈低表达,是2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的保护因素,二者联合对2型糖尿病患者发生DKD有一定预测价值。样本量较小为本研究不足之处,eNOS、Omentin-1在DKD中的临床价值,后续将扩大样本量进行前瞻性研究验证。
-
表 1 对照组和DKD组患者临床指标比较
Table 1 Comparison of clinical parameters between control and DKD groups
指标 对照组(n=125) DKD组(n=124) χ2/t值 P值 年龄(岁,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 52.80 ± 8.70 53.50 ± 8.50 0.642 0.521 男性(例) 60 68 1.165 0.280 BMI(kg/m2,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 26.24 ± 3.36 25.81 ± 3.15 1.042 0.299 SBP(mmHg,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 131.21 ± 9.31 129.84 ± 8.17 1.234 0.218 DBP(mmHg,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 89.43 ± 12.21 87.45 ± 11.32 1.327 0.186 TC(mmol/L,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 4.48 ± 0.96 4.75 ± 0.91 2.277 0.024 FPG(mmol/L,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 8.48 ± 1.57 8.51 ± 1.54 0.152 0.879 HbA1c(%,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 8.56 ± 1.23 9.32 ± 1.25 4.836 <0.001 24 h尿蛋白定量(g,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 0.15 ± 0.02 2.78 ± 0.31 94.656 <0.001 mAlb(mg/L,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 23.08 ± 3.35 273.12 ± 20.41 135.148 <0.001 Scr(μmol/L,$\bar{x} \pm s $) 73.52 ± 9.21 209.53 ± 22.59 62.298 <0.001 eGFR[mL·min−1·(1.73 m2)−1,$\bar{x} \pm s $] 107.34 ± 10.27 72.52 ± 13.51 22.906 <0.001 注:DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;BMI为体重指数;SBP为收缩压;DBP为舒张压;TC为总胆固醇;FPG为空腹血糖;HbA1c为糖化血红蛋白;mAlb为尿微量白蛋白;Scr为血肌酐;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率;1 mmHg=0.133 kPa。 表 2 对照组和DKD组患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1水平比较($\bar{x} \pm s$)
Table 2 Comparison of serum levels of eNOS and Omentin-1 between control and DKD groups($\bar{x} \pm s $)
组别 例数 eNOS(U/L) Omentin-1(μg/L) 对照组 125 33.82 ± 4.52 43.63 ± 6.78 DKD组 124 24.48 ± 3.37 28.75 ± 4.42 t值 - 18.474 20.497 P值 - <0.001 <0.001 注:DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;eNOS为内皮型一氧化氮合酶;Omentin-1为网膜素1。 表 3 DKD患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1和临床指标的相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of serum levels of eNOS and Omentin-1 and clinical parameters in DKD patients
指标 eNOS Omentin-1 r值 P值 r值 P值 TC −0.152 0.141 −0.113 0.136 HbA1c −0.085 0.203 −0.173 0.105 24 h尿蛋白定量 −0.456 <0.001 −0.551 <0.001 mAlb −0.503 <0.001 −0.527 <0.001 Scr −0.497 <0.001 −0.495 <0.001 eGFR 0.523 <0.001 0.602 <0.001 Omentin-1 0.674 <0.001 - - 注:DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;eNOS为内皮型一氧化氮合酶;Omentin-1为网膜素1;TC为总胆固醇;HbA1c为糖化血红蛋白;mAlb为尿微量白蛋白;Scr为血肌酐;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率。 表 4 影响2型糖尿病患者发生DKD的多因素Logistic回归分析
Table 4 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of DKD occurrence in T2DM patients
自变量 B值 SE值 Wald值 OR值 95% CI P值 TC 0.054 0.273 0.039 1.056 0.618~1.803 0.841 HbA1c 0.450 0.297 2.300 1.569 0.877~2.808 0.129 24 h尿蛋白定量 0.950 0.305 9.712 2.587 1.423~4.703 0.001 mAlb 1.104 0.413 7.140 3.015 1.342~6.774 0.007 Scr 0.976 0.324 9.075 2.654 1.406~5.008 0.002 eGFR −0.247 0.105 5.541 0.781 0.635~0.959 0.019 eNOS −0.365 0.117 9.747 0.694 0.552~0.873 0.002 Omentin-1 −0.346 0.124 7.818 0.707 0.554~0.901 0.005 注:DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;TC为总胆固醇;HbA1c为糖化血红蛋白;mAlb为尿微量白蛋白;Scr为血肌酐;eGFR为估算肾小球滤过率;eNOS为内皮型一氧化氮合酶;Omentin-1为网膜素1。 表 5 2型糖尿病患者血清eNOS、Omentin-1水平对DKD发生的预测价值
Table 5 Predictive value of serum levels of eNOS and Omentin-1 for DKD occurrence in T2DM patients
指标 AUC 95%CI 截断值 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 约登指数 eNOS(U/L) 0.882 0.835~0.919 29.60 77.42 82.40 0.598 Omentin-1(μg/L) 0.862 0.812~0.902 36.93 81.45 77.60 0.591 二者联合 0.942 0.906~0.968 - 92.74 80.80 0.735 注:eNOS为内皮型一氧化氮合酶;Omentin-1为网膜素1;DKD为糖尿病肾脏疾病;AUC为曲线下面积。 -
[1] 邵晓琳,罗雨轻,马东红,等. 糖尿病肾脏疾病患者的光镜下肾小管病变与临床指标关系及对预后的影响[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志,2022,22(11):903-910.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.2022.11.004. Shao XL,Luo YQ,Ma DH,et al. Associations between renal tubular lesions and clinical parameters as well as prognosis in diabetic kidney disease[J]. J Clin Nephrol,2022,22(11):903-910. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.2022.11.004.
[2] Liu SL,Premont RT,Park KH,et al. β-PIX cooperates with GIT1 to regulate endothelial nitric oxide synthase in sinusoidal endothelial cells[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol,2022,323(5):G511-G522. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00034.2022.
[3] 景梦怡,王俭勤,梁耀军,等. 微RNA-155在db/db小鼠体内的表达及其作用[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志,2020,36(6):463-470.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441217-20191112-00086. Jing MY,Wang JQ,Liang YJ,et al. Expression and role of microRNA-155 in db/db mice[J]. Chin J Nephrol,2020,36(6):463-470. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441217-20191112-00086.
[4] Eimal Latif AH,Anwar S,Gautham KS,et al. Association of plasma omentin-1 levels with diabetes and its complications[J]. Cureus,2021,13(9):e18203. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.18203.
[5] 孙军萍,黎宗保,韩耀光,等. 妊娠糖尿病患者血清Omentin-1、IRS-1、IRS-2与胰岛素抵抗的关系[J]. 中国妇产科临床杂志,2020,21(1):83-84.DOI: 10.13390/j.issn.1672-1861.2020.01.031. Sun JP,Li ZB,Han YG,et al. Relationship between serum Omentin-1, IRS-1, IRS-2 and insulin resistance in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus[J]. Chin J Clin Obstet Gynecol,2020,21(1):83-84. DOI: 10.13390/j.issn.1672-1861.2020.01.031.
[6] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会微血管并发症学组. 中国糖尿病肾脏病防治指南(2021年版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2021,13(8):762-784.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20210706-00369. Microvascular Complications Group of Chinese Diabetes Society. Clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of diabetic kidney disease in China (2021 edition)[J]. Chin J Diabetes Mellit,2021,13(8):762-784. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20210706-00369.
[7] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志,2018,38(4):292-344.DOI: 10.19538/j.nk2018040108. Chinese Diabetes Society. Guidelines for the prevention and control of type 2 diabetes in China(2017 Edition)[J]. Chin J Pract Intern Med,2018,38(4):292-344. DOI: 10.19538/j.nk2018040108.
[8] 胡丹,樊友文,涂卫平. 5种肾小球滤过率评估方程在2型糖尿病人群中的应用[J]. 中国实用内科杂志,2020,40(9):744-748.DOI: 10.19538/j.nk2020090109. Hu D,Fan YW,Tu WP. Performance of five estimated glomerular filtration rate equations in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chin J Pract Intern Med,2020,40(9):744-748. DOI: 10.19538/j.nk2020090109.
[9] 朱娜. 2型糖尿病患者合并肾脏病变的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志,2022,22(3):228-232.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.2022.03.009. Zhu N. Clinicopathologic features and prognoses of type 2 diabetics with renopathy[J]. J Clin Nephrol,2022,22(3):228-232. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.2022.03.009.
[10] Luo M,Lin HC,Wen ZQ,et al. Sodium ferulate inhibits rat cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by angiotensin II through enhancement of endothelial nitric oxide synthase/nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate signaling pathway[J]. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol,2022,80(2):251-260. DOI: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001277.
[11] 胡玲,王思思,周乐汀,等. eNOS基因G894T多态性与糖尿病肾病易感性的荟萃分析[J]. 临床与病理杂志,2021,41(3):623-632.DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2021.03.021. Hu L,Wang SS,Zhou LT,et al. Associations between eNOS gene G894T polymorphism and susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy: a Meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Pathol Res,2021,41(3):623-632. DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2021.03.021.
[12] Chakkarwar VA,Kawtikwar P. Fenofibrate prevents nicotine-induced acute kidney injury: possible involvement of endothelial nitric oxide synthase[J]. Indian J Nephrol,2021,31(5):435-441. DOI: 10.4103/ijn.IJN_380_20.
[13] 阚启明,胡耀豪,何仲贵. 增进eNOS二聚体活性进而改变NO与ONOO-比例是治疗糖尿病肾病的新方向[J]. 生理学报,2022,74(1):93-109.DOI: 10.13294/j.aps.2022.0009. Kan QM,Hu YH,He ZG. Normalization of the ratio of nitric oxide and peroxynitrite by promoting eNOS dimer activity is a new direction for diabetic nephropathy treatment[J]. Acta Physiol Sin,2022,74(1):93-109. DOI: 10.13294/j.aps.2022.0009.
[14] Lin SY,Li X,Zhang JB,et al. Omentin-1: protective impact on ischemic stroke via ameliorating atherosclerosis[J]. Clin Chim Acta,2021,517:31-40. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2021.02.004.
[15] Song J,Zhang HX,Sun YN,et al. Omentin-1 protects renal function of mice with type 2 diabetic nephropathy via regulating miR-27a-Nrf2/Keap1 axis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2018,107:440-446. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.002.
[16] 徐静. 血浆omentin-1水平与糖尿病外周动脉疾病的相关性研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北医科大学, 2021. DOI: 10.27111/d.cnki.ghyku.2021.000748. Xu J. The Association between Omentin-1 Level and Peripheral Artery Disease in Diabetes Mellitus[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Medical University, 2021. DOI: 10.27111/d.cnki.ghyku.2021.000748.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 蔡晓盛,周觉,陶凯. 瑞舒伐他汀对吸烟合并2型糖尿病患者血管内皮功能及血液流变学的影响. 全科医学临床与教育. 2025(01): 27-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)







 下载:
下载:

.png)