Comprehensive analysis of ferroptosis patterns and immunologic characteristics in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis
-
摘要:目的
探究抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体(anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, ANCA)相关性血管炎(anca-associated vasculitis, AAV)伴肾损伤中铁死亡亚型及在免疫微环境的作用,为开发新的免疫治疗提供基础。
方法从GEO数据库下载关于AAV的肾脏数据集。基于差异表达的结果上,共识聚类算法用于铁死亡亚型的鉴定。采用单样本基因集富集分析和基因集变异分析算法来评估亚型的免疫浸润和信号通路。进一步由LASSO、SVM-RFE算法筛选关键的铁死亡特征基因(ferroptosis related genes, FRGs),并由独立数据集进行验证。CIBERSORT用于评估FRGs的浸润免疫细胞的丰度。最后,由rsm包构建FRGs的临床诊断性模型,使用 Nephroseq V5 数据库分析FRGs与肾功能之间的相关性。
结果24个铁死亡相关基因在AAV伴肾损伤中显著差异表达,无监督聚类分析确定了两种不同铁死亡亚型,其在基因表达、免疫浸润、生物功能通路上存在显著差异。进一步筛选了一个由 ALOX5、CD44、CRYAB、TP53和FTH1组成的FRGs集,其可有效地区分AAV伴肾损伤和正常对照组。趋化因子受体、巨噬细胞和HLA等与FRGs呈显著正相关。由FRGs构建的临床诊断模型的受试者工作特征曲线的曲线下面积为0.961,而且其与肾小球滤过率均呈负相关;除了CRYAB、FTH1外,其他FRGs与血肌酐均呈正相关,表明它们可能与AAV的肾损伤密切相关,是预后生物标志物。
结论本研究发现AAV伴肾损伤中铁死亡与免疫微环境密切相关,为更好地了解铁死亡模式而开发新的AAV 伴肾损伤的治疗方案奠定了基础。
-
关键词:
- 抗中性粒细胞胞浆抗体相关性血管炎 /
- 肾损伤 /
- 铁死亡 /
- 免疫特征 /
- 计算生物学
Abstract:ObjectiveTo lay the groundwork for formulating novel immunotherapies through understanding the regulatory role of ferroptosis and its function in immune microenvironment in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) with renal injury.
MethodsKidney data sets on AAV were downloaded from the database of Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Based upon the results of differential expression, consensus clustering algorithm was employed for identifying the subtypes of iron mortality. Single sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) and gene set variation analysis (GSVA) were performed for evaluating the immune invasion and signaling pathways of subtypes. Key ferroptosis-related genes (FRGs) were further screened by LASSO and SVM-RFE algorithms and verified by independent data sets. CIBERSORT was utilized for assessing the abundance of infiltrating immune cells for FRGs. Finally a clinical diagnostic model of FRGs was constructed by rsm package. And the correlation between FRGs and renal function was examined by Nephroseq V5 database.
ResultsTwenty-four ferroptosis related genes were significantly differentially expressed in AAV with kidney injury. Unsupervised cluster analysis revealed the regulatory patterns of two different ferroptosis subtypes with significant differences in gene expression, immune infiltration and biological functional pathways. A set of FRGs composed of ALOX5, CD44, CRYAB, TP53, and FTH1 was selected by two machine learning algorithms. It could effectively distinguish AAV with kidney injury from normal control group. CCR, macrophage and HLA were correlated positively with FRGs. Area under ROC curve of clinical diagnostic model constructed by FRGs was 0. 961. FRGs were correlated negatively with glomerular filtration rate (GFR). However, except for CRYAB and FTH1, other FRGs were correlated positively with serum creatinine (Scr). It implicated their potential relevance to renal injury in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) and their potential as prognostic biomarkers.
ConclusionsFerroptosis in AAV with kidney injury is correlated closely with immune microenvironment. It provides rationales for devising new treatments for AAV with kidney injury through a better understanding the pattern of ferroptosis.
-
抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体(anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, ANCA)相关性血管炎(ANCA-associated vasculitis,AAV)是一种小血管炎,包括肉芽肿性多血管炎、显微镜下多血管炎和嗜酸性肉芽肿性多血管炎[1]。75% 以上AAV患者存在肾脏受累,急性肾损伤(acute kidney injury,AKI)是AAV的严重并发症,其可导致终末期肾病,甚至死亡[2]。尽管糖皮质激素和其他免疫抑制药物可以提高AAV患者的生存率,但免疫抑制治疗的不良反应现在仍然是 AAV患者早期死亡的主要原因[3]。而且AAV 的肾脏预后仍然不理想,20% ~25% 的患者会出现肾衰竭[4],因此探究新的AAV伴肾损伤的治疗方法是一个重要的方向。
铁死亡是一种新发现的程序性细胞死亡形式,其特征是铁依赖性脂质过氧化氢累积至致死水平。最近,有研究发现铁死亡参与了AKI的各种病理模型,体内和体外实验表明,铁死亡抑制剂对肾损伤有效[5-6]。GPX4缺失的小鼠可自发发展AKI[7],而谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4上调可防止AKI的发生[8]。同时,Zhang等[8]发现在白细胞介素 1 受体基因缺失的 KPKD1小鼠中,一种特异性铁死亡抑制剂Nec-1 对铁死亡的抑制导致肾脏重量增加和囊肿形成加速。铁死亡诱导剂与肿瘤也密切相关,有研究发现肾透明细胞癌对铁死亡诱导剂特别敏感,其可能通过上调抗铁死亡途径来逃避高过氧化氢负荷所致的损伤[9]。综上所述,铁死亡与肾脏疾病联系紧密,而且参与了AKI的发生发展,而AKI是AAV伴肾损伤主要的并发症之一。因此,铁死亡可能成AAV伴肾损伤的一种新的治疗方向。鉴于以往没有关于铁死亡在AAV伴肾损伤中作用的研究,本研究探讨了AAV伴肾损伤中铁死亡调控模式及在免疫微环境中的作用,为开发新的免疫治疗提供基础。
在本研究中,通过GEO数据库下载AAV伴肾损伤中铁死亡的数据。首先对差异表达的铁死亡基因进行富集分析,并通过共识聚类算法鉴定不同铁死亡亚型,并探讨其在基因表达、免疫微环境、生物功能通路上的差异。进一步由LASSO回归和SVM-RFE算法鉴定关键的铁死亡特征基因,为明确其临床决策能力,构建了临床诊断模型。最后,探索关键的铁死亡特征基因与肾功能的相关性,明确其预后价值。
对象与方法
一 数据来源及预处理
从GEO数据库(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)和Array Express数据库(https://www.ebi.ac.uk/biostudies/arrayexpress)中下载AAV伴肾损伤的患者和健康供体的基因表达数据,主要包含了四个数据集(GSE104954、GSE108112、GSE104948、E-MTAB-1944)。GSE104954包含 42 个肾小管间质样本,包括 21个AAV 样本,21个活体健康供体样本[10];GSE108112包含 62个肾小管间质样本,包括 57个AAV 样本,5个活体健康供体样本[10];GSE104948包含43个肾小球样本,21个活体健康供体样本和22个AAV样本[10];E-MTAB-1944包含 42 个全肾组织样本,包括30 个AAV样本和12 个活体健康供体样本[11]。首先,将GSE108112和GSE104954合并为一个数据集以作为训练集,GSE104948、E-MTAB-1944作为独立验证数据集。通过 “Combat”算法消除批次效应[12]。从FerrDb数据库(http://www.zhounan.org/ferrdb/current/)中下载了259 个铁死亡基因,包括108个驱动基因,69个抑制基因和111个基因标志物。
二 差异表达分析
使用R中的 limma 包进行差异表达分析,选取阈值FDR<0.01。筛选出差异表达的铁死亡基因(differentially expressed ferroptosis genes, DE-FGs),并用ggplot2 包绘制火山图。
三 DE-FGs功能富集分析
使用R的“clusterProfiler”和“enrichment plot”包对DE-FGs进行GO分析、KEGG分析。
四 铁死亡亚型的鉴定和生物学功能分析
根据DE-FGs的表达矩阵,R 包“Consensu Cluster Plus”被用来进行无监督聚类分析以识别不同的铁死亡亚型[13]。通过主成分分析(principal component analysis, PCA)以进一步验证在不同亚型下的表达模式。HALLMARKS通路被用来反映生物变化。通过GSVA算法将表达矩阵转换为通路激活评分矩阵,并通过R包“limma”比较两组之间的通路激活评分[14]。从 MSigDB 数据库下载“h.all.v7.0.symbols”基因集用于GSVA 分析。
五 铁死亡特征基因的鉴定和验证
关键FRGs由LASSO回归[15]和SVM-RFE[16]两种机器学习算法来鉴定,通过独立的数据集E-MTAB-1944及GSE104948进行验证其差异表达,受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve, ROC)曲线下面积用于评估其诊断效能。
六 免疫特征的相关性分析
单样本基因集富集分析用于估计特定浸润免疫细胞的数量和特定免疫反应的活性[17]。浸润的免疫细胞基因集来自之前的研究[18]。
七 临床诊断性模型的构建和临床肾功能的相关性分析
将GSE108112和GSE104954合并后的数据集作为模型构建样本,使用“rms”包构建列线图。通过ROC曲线来评估模型的鉴别能力。利用校准曲线和决策曲线分析评价模型的临床价值。通过下载FRGs的表达数据,结合Nephroseq V5数据库中肾功能的数据,FRGs与肾小球滤过率(glomerular filtration rate, GFR)、血肌酐(serum creatinine,Scr)之间的相关性被进一步分析,由“ggplot2”绘制散点图。
八 统计分析
所有分析均在R 4.1.2中进行。两组或多组间分别采用Wilcoxon或Kruskal-Wallis检验进行比较。当数据为非正态分布时,采用Mann-Whitney检验。FRGs与免疫细胞分数和临床肾功能之间的相关性,采用Spearman相关分析。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结 果
一 DE-FGs的鉴定
本研究共纳入铁死亡基因有259个,24个铁死亡基因在正常样本与AAV伴肾损伤样本中显著差异表达(图1A)。由火山图可见,24个差异表达的铁死亡基因(DE-FGs)中有12个上调基因,12个下调基因,其中 ALOX5具有最大的logFC,而TP53变化较大(图1B)。我们注意到DE-FGs之间的联系非常密切,CD44与ALOX5呈正相关(R=0.77,P<0.05);HSBP1和ACSF2呈负相关(R=−0.76,P<0.05),它们是相关性最高的两对FRGs。表明它们可能一起发挥作用(图1C)。
二 DE-FGs的功能分析
为了阐明与DE-FGs的相关的生物学功能,进行了GO 和 KEGG富集分析。 其中GO 富集分析表明,在生物过程中,DE-FGs与“对氧化应激的反应”“细胞衰老”“对金属离子的反应”相关;在分子功能方面,与“病毒受体活性”“外源性蛋白的结合”和“连接酶的活性”相关;而在细胞组成中,与“细胞基底部”“细胞基膜”和“板状伪足膜”相关(图2A)。KEGG富集分析表明,DE-FGs主要在“铁死亡”“流体剪切应力和动脉粥样硬化”、“谷胱甘肽代谢”“矿物质的吸收和辅助因子的生物合成”得到了富集(图2B)。 这些证据表明,DE-FGs可能通过铁死亡、流体剪切应力、谷胱甘肽代谢、氧化应激等在 AAV伴肾损伤中发挥作用。
三 铁死亡亚型的鉴定
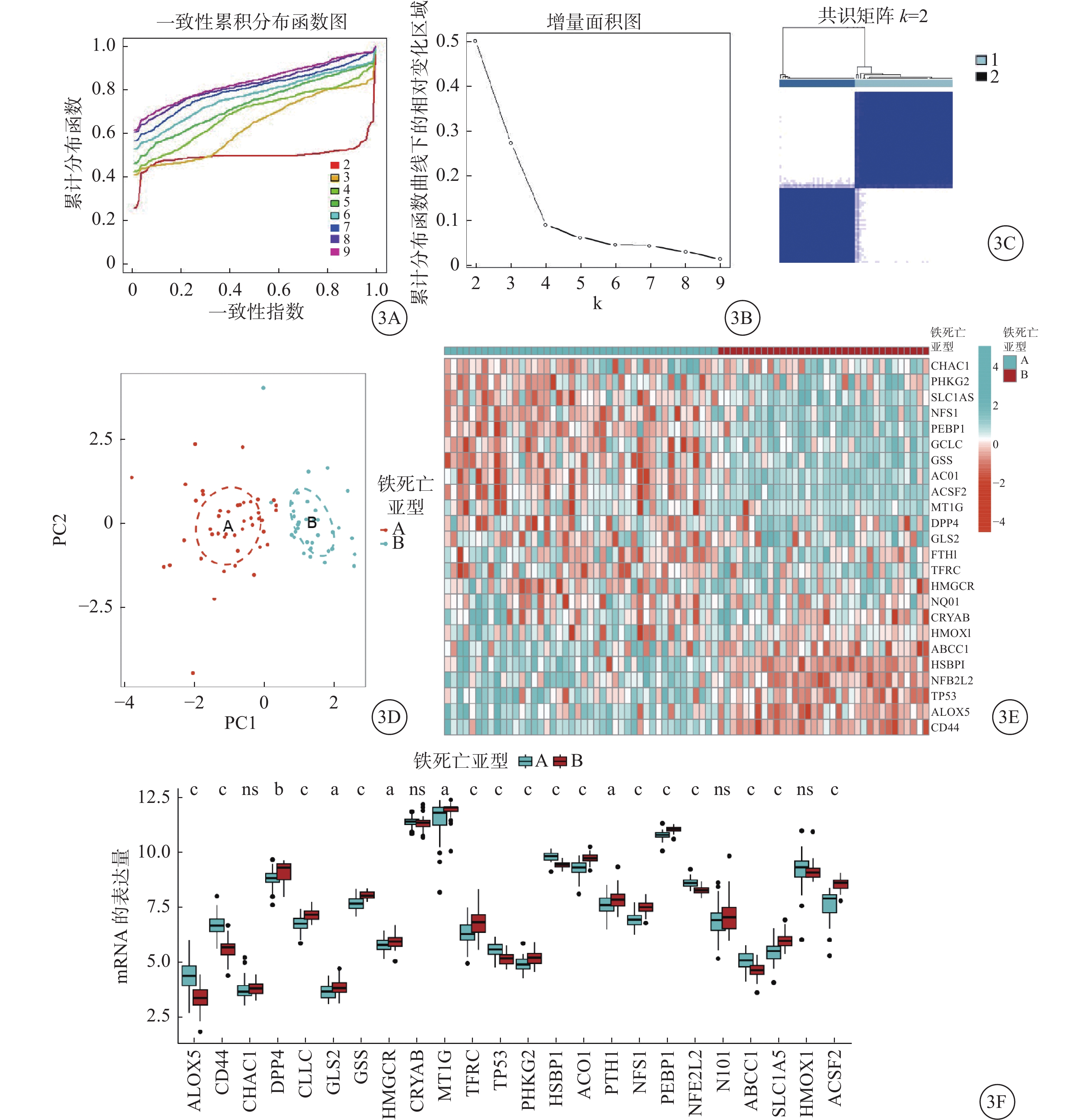
为了探究AAV伴肾损伤中铁死亡亚型,我们基于 24个DE-FGs的表达量对AAV伴肾损伤样本进行了无监督共识聚类分析。结合累积分布函数和共识聚类矩阵热图,k=2是一个充分的选择,两种不同的AAV伴肾损伤铁死亡亚型被鉴定(图3A~C)。在PCA中,两种铁死亡亚型有显著不同的人群(图3D)。除 CHAC1、CRYAB、NQO1、HMOX1外,其他所有基因在两种铁死亡亚型之间的表达差异有统计学意义(图3E~F),验证了AAV伴肾损伤中存在多样性铁死亡调控模式。
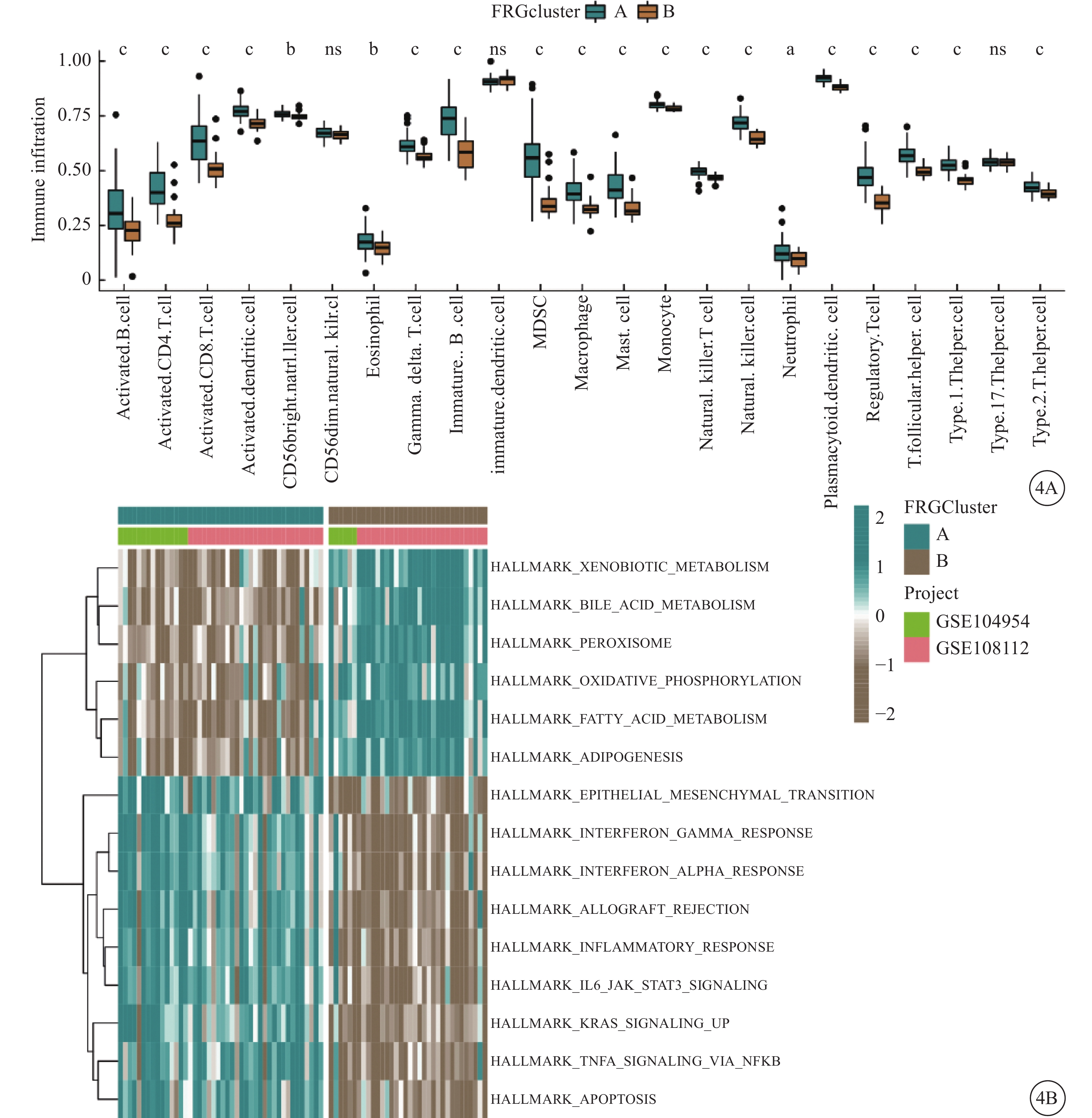
四 不同铁死亡亚型的免疫特征和生物学功能
为了进一步确定两种铁死亡亚型的免疫特征,我们比较了两种不同铁死亡亚型之间的浸润免疫细胞的丰度。与亚型B相比,亚型A具有较高的浸润免疫细胞。有趣的是,除了CD56dim 自然杀伤细胞、未成熟的树突状细胞和17 型辅助 T 细胞外,所有的免疫浸润细胞在两种铁死亡亚型中显著差异表达,而且在亚型A中均具有更高水平(图4A)。表明铁死亡亚型A可能在AAV伴肾损伤中免疫组。为了研究不同铁死亡亚型潜在的生物功能,我们进行了 GSVA 来评估富集的生物通路,图4B显示了两种亚型之间HALLMARKS通路的富集差异。上皮间充质转变、干扰素γ反应、炎症反应、IL-6-JAK-STAT3信号通路、通过NF-κB介导TNF-a信号通路及KRAS 信号通路均在亚型 A中更富集,而外源化合物代谢、胆汁酸代谢和氧化磷酸化等在亚型B中更富集。应该指出的是,亚型B高度富集在物质代谢相关通路,而亚型A主要富集在免疫相关通路。上述结果再次证明铁死亡对AAV伴肾损害的不同免疫微环境的塑造具有重要的调控作用。
五 铁死亡特征基因的鉴定和验证
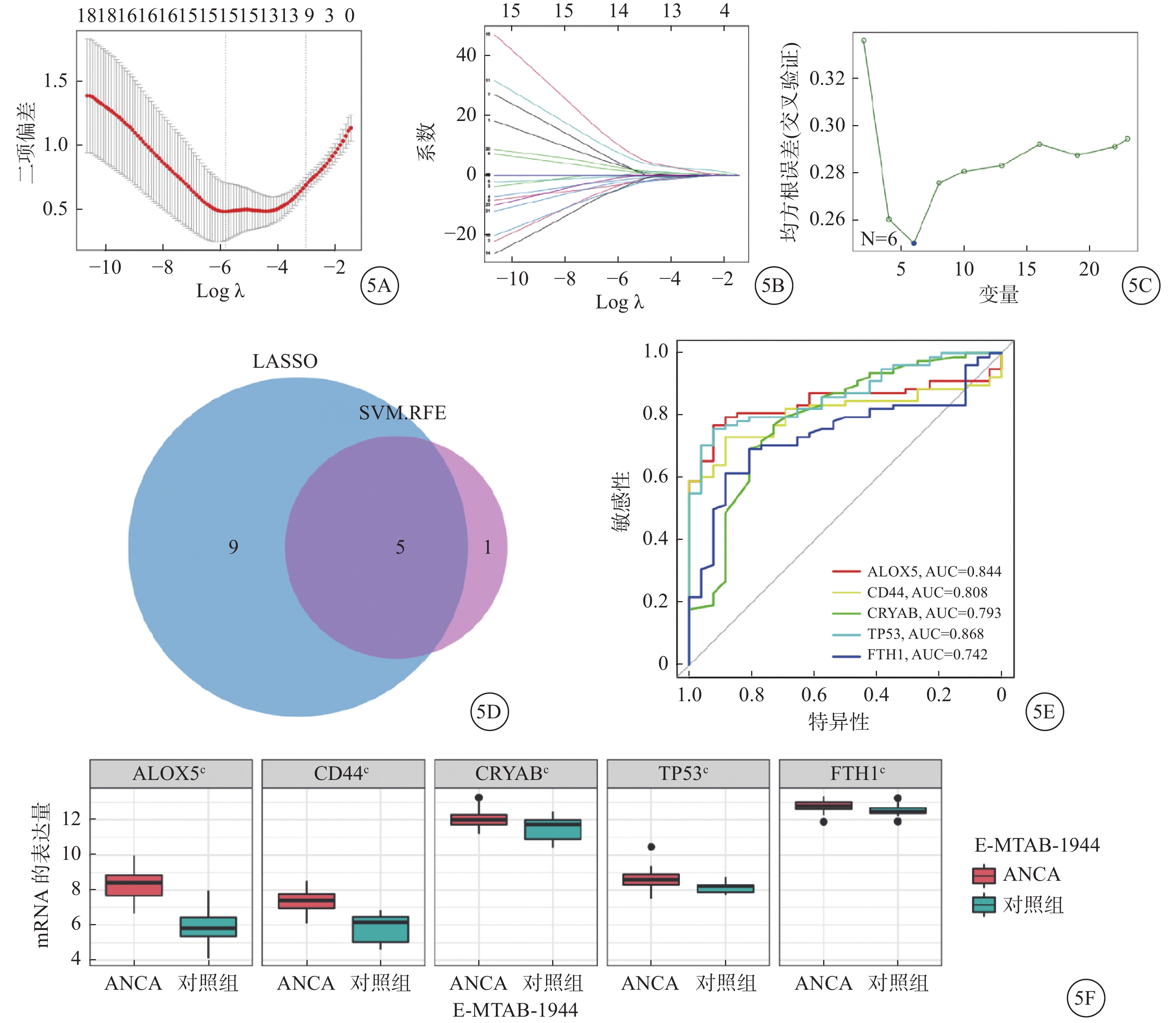
为了明确在AAV伴肾损伤中的铁死亡特征基因,采用两种机器学习算法,LASSO回归用于进行特征选择和降维,以便排除不重要的调节因子。在差异分析的基础上,我们将24个DE-FGs通过LASSO回归筛选得到14个重要的铁死亡基因(图5A~B )。同时将24个DE-FGs进行SVM-RFE算法筛选,以识别AAV伴肾损伤的特征基因(图5C),我们发现有6个重要的铁死亡基因。最终,从 LASSO 和 SVM-RFE 算法中获得的重要基因进行交叉,确定了5个铁死亡特征基因(ALOX5、CD44、CRYAB、TP53、FTH1)用于后续分析(图5D)。通过独立验证集GSE104948验证5个FRGs的诊断效能,我们发现TP53、CD44、ALOX5的曲线下面积均大于0.9(图5E),表明其在区分健康和AAV伴肾损伤样本方面表现良好。同时E-MTAB-1944数据集验证了5个FRGs均在AAV伴肾损伤中显著差异表达(图5F)。因此,FRGs可能在AAV伴肾伤中发挥重要作用。
六 铁死亡特征基因与免疫细胞浸润相关性分析
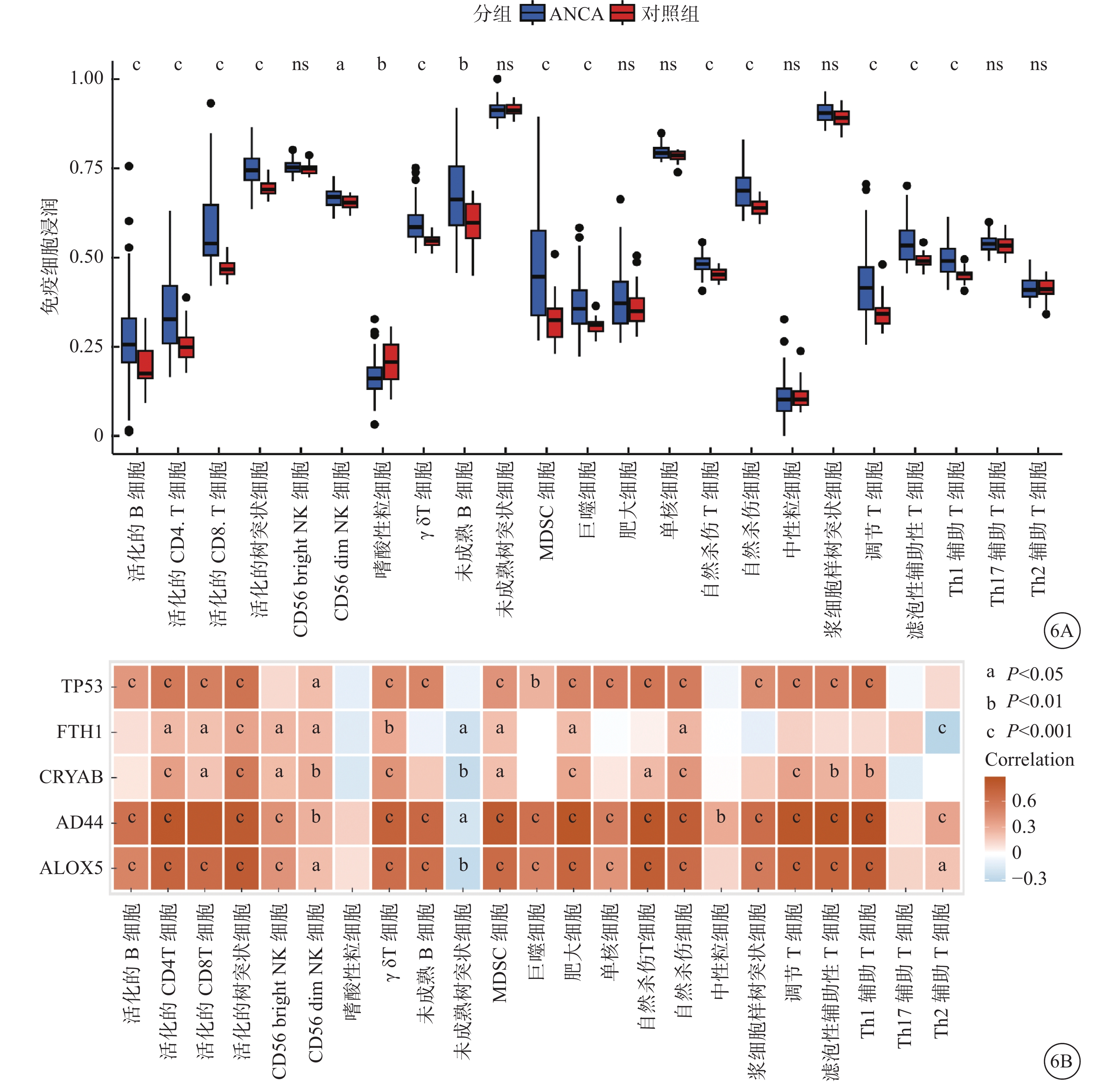
为了进一步阐明在AAV伴肾损伤和正常对照组之间免疫浸润的差异。通过CIBERSORT算法,我们发现抗原递呈细胞的协同刺激、趋化因子受体、免疫检查点、细胞杀伤活性、HLA、巨噬细胞、I类主要组织相容性复合体、中性粒细胞、副炎症等在AAV伴肾损伤和正常对照组之间存在显著差异,而且均高于正常对照组(图6A)。值得注意的是,通过进一步分析5个FRGs与免疫浸润的相关性时,得到一致的结果。抗原递呈细胞的协同刺激、趋化因子受体、免疫检查点、细胞杀伤活性、HLA、巨噬细胞、I类主要组织相容性复合体、中性粒细胞、副炎症均与CD44、ALOX5、TP53呈显著正相关,而与FTH1和CRYAB相关性不强。其中CRYAB与抗体-药物偶联物呈显著负相关(图6B)。表明FRGs与免疫浸润密切相关。
七 临床诊断性模型的构建和临床肾功能的相关性分析
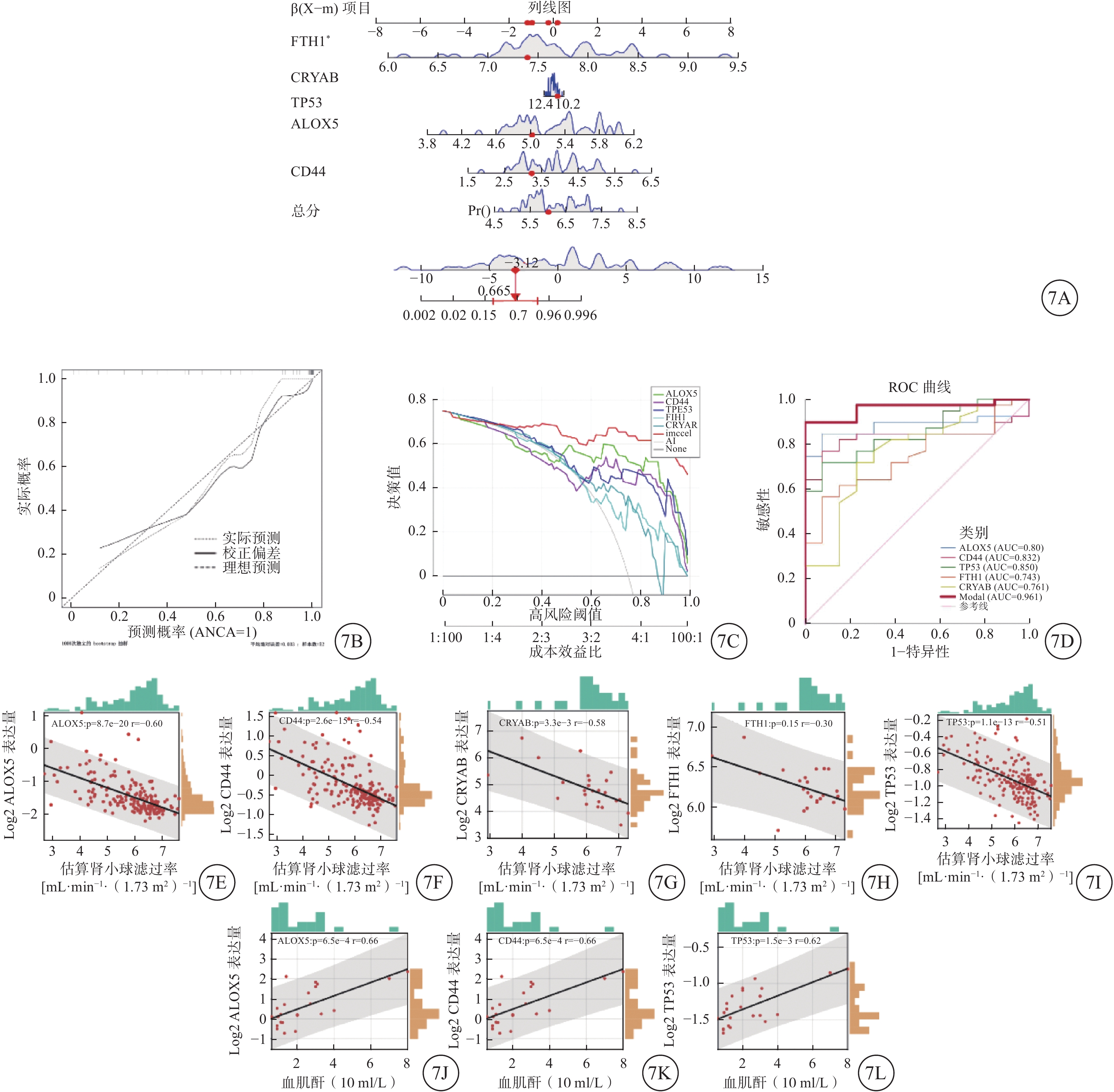
将GSE108112和GSE104954合并后的104例患者作为模型样本。由5个FRGs(CD44、FTH1、CRYAB、ALOX5、TP53)参与临床诊断模型的构建(图7A)。使用校准曲线评估模型的校准能力,该校准曲线显示实际的AAV伴肾损伤风险与预测风险之间的差异较小(图7B)。采用临床决策曲线分析评估患者的临床决策效益。DCA曲线上0到1的高风险阈值显示橙色线高于灰色线,高于每个单独的FRGs,这表明该模型可以从临床决策中受益(图7C)。采用ROC曲线测量模型的鉴别能力,模型的曲线下面积约为0.961,高于任何一个FRGs,表明模型具有较高的诊断效能(图7D)。为了进一步探究FRGs与肾功能的关系,通过Nephroseq数据库提取FRGs的相对表达量、GFR和Scr水平。由于Nephroseq V5数据库缺乏FTH1、CRYAB的表达量与Scr水平的数据,因此探究了ALOX5、CD44、TP53与Scr之间的相关性。Spearman相关性分析发现(图7E~I),5个FRGs均与GFR呈负相关,ALOX5、CD44、TP53与Scr均呈正相关(图7J~L),提示这些基因与AAV患者的肾功能密切相关,是AAV伴肾损伤潜在的预后生物标志物。
讨 论
AAV是一组以肉芽肿性和中性粒细胞组织炎症为特征的小血管炎,通常与ANCA的产生有关。AAV常累及全身多个脏器,以肾脏和肺的累及最为突出,也最为凶险。许多研究已经证实,铁死亡在疾病,尤其是恶性肿瘤的发展中发挥着关键作用[19]。然而,关于AAV伴肾损伤中铁死亡的研究很少。本研究探究了铁死亡在AAV伴肾损伤中的作用,并揭示了铁死亡与免疫特征的关联。
在本研究中,基于差异表达的铁死亡基因表达谱,使用无监督聚类法鉴定了两种不同的铁死亡亚型。在免疫浸润中,大部分免疫细胞显示出明显的差异。相对于亚型B而言,亚型A有更高丰度的免疫细胞浸润。亚型A可能是AAV伴肾损伤中的免疫组,而亚型B为非免疫组。有趣的是,在功能通路上发现相同的结果,亚型 A在干扰素γ反应、IL-6-JAK-STAT3信号通路、通过NF-κB介导TNF-α信号通路等中更富集,而外源化合物代谢、胆汁酸代谢和氧化磷酸化等在亚型B中更加富集。有研究发现,肾小管间质中 CD56自然杀伤细胞产生干扰素γ促进肾纤维化和慢性肾病进展[20],提示干扰素γ可能通过CD56细胞加重AAV伴肾损伤的进程。一项回归性研究发现IL-6 在活动性血管炎部位表达和产生增加,通过托珠单抗治疗能够使严重多系统MPA 患者的疾病完全和持续缓解,并使 IL-6相关的细胞因子和趋化因子的循环水平正常化[21]。既往的研究发现TNF-α可能在中性粒细胞启动中起作用,导致内皮细胞黏附分子和ANCA抗原在细胞表面的表达,从而促进AAV的发生发展,与本研究结果一致[22]。以上结果表明亚型A中的免疫相关的信号通路可能在AAV伴肾损伤中发挥重要作用。
通过两种机器学习算法筛选出5个铁死亡特征基因,包括CD44、CRYAB、FTH1、TP53和ALOX5。其中CD44主要编码的蛋白质是一种细胞表面糖蛋白,参与细胞间相互作用、细胞黏附和迁移[23]。Kato等[24]发现抑制 T 细胞上的黏附分子 CD44,可抑制 T 细胞活性和细胞浸润。有研究发现去分化脂肪细胞的植入可降低了AAV小鼠肾脏中 CD44 mRNA 的表达,其可能通过抑制 T 细胞的活性和侵袭来调节免疫活性[25]。与本研究结果一致,表明CD44可能通过T细胞在AAV伴肾损伤中发挥重要作用。CRYAB是哺乳动物晶状体蛋白,是小热休克蛋白家族的成员。Justin等[26]报道CRYAB抑制肾脏炎症并保护易患狼疮的 NZB/W F1 小鼠免受肾损伤。说明CRYAB可能与AAV的肾脏炎症反应密切相关。FTH1主要编码铁蛋白的重链亚基。有研究发现通过敲除FTH1来补充肾脏巨噬细胞中的不稳定铁池,可减轻肾脏的氧化应激和纤维化[27]。TP53主要编码包含转录激活、DNA 结合和寡聚化结构域的肿瘤抑制蛋白。在肾透明细胞癌中,TP53与增加的细胞周期和合成代谢密切相关[28]。ALOX5主要为编码脂肪氧化酶基因家族的一个成员,并在花生四烯酸合成白三烯中发挥作用。在肾透明细胞癌的患者中,ALOX5的表达升高预示着患者的存活率降低,并且与健康组织样本相比,始终发现肿瘤样本中的 ALOX5 表达上调[29]。目前的研究支持TP53和ALOX5与肾脏肿瘤密切相关。本研究发现TP53和ALOX5不仅与趋化因子受体、巨噬细胞和HLA等呈显著正相关,而且与GFR均呈显著负相关,其可能通过巨噬相关免疫反应参与AAV的肾损伤过程。然而,关于TP53和ALOX5如何在AAV伴肾损害发生发展中作用仍有待进一步研究。总之,这些发现表明FRGs在AAV伴肾损害的发生发展中起重要作用,并且有助于阐明AAV伴肾损伤的发病机制和开发用于诊断和靶向治疗的新生物标志物。
该研究有一定的局限性。首先,由于缺乏每位患者的临床信息,如性别、年龄、治疗方案、临床分型、肾功能、预后等,无法对所有样本的铁死亡模式、临床分型和其他临床特征进行相关分析。其次,尽管该研究合并多中心的数据,但样本量仍不够,未来仍需要更大样本量的研究。 此外,基于AAV伴肾损伤和健康样本的研究,主要通过生物信息学分析获得,这需要进一步的基础实验验证。
总之,本研究通过观察到健康个体和AAV伴肾损害患者之间大多数铁死亡基因的表达存在显著差异。由无监督聚类法鉴定出两种生物学功能不同的铁死亡亚型,其中亚型A与免疫密切相关。通过两种机器学习算法确定了五个铁死亡特征基因,它们不仅与免疫细胞浸润和临床肾功能密切相关,同时以其构建的临床诊断模型可为临床决策提供参考。
-
-
[1] Jennette JC,Falk RJ,Bacon PA,et al. 2012 revised international chapel hill consensus conference nomenclature of vasculitides[J]. Arthritis Rheum,2013,65(1):1-11. DOI: 10.1002/art.37715.
[2] Hruskova Z,Stel VS,Jayne D,et al. Characteristics and outcomes of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (wegener) and microscopic polyangiitis requiring renal replacement therapy: results from the European renal association–european dialysis and transplant association registry[J]. Am J Kidney Dis,2015,66(4):613-620. DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.03.025.
[3] Geetha D,Jefferson JA. ANCA-associated vasculitis: core curriculum 2020[J]. Am J Kidney Dis,2020,75(1):124-137. DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.04.031.
[4] Lionaki S,Hogan SL,Jennette CE,et al. The clinical course of ANCA small-vessel vasculitis on chronic dialysis.[J]. Kidney international,2009,76(6):644-51. DOI: 10.1038/ki.2009.218.
[5] Martin-Sanchez D,Ruiz-Andres O,Poveda J,et al. Ferroptosis, but Not Necroptosis, Is Important in Nephrotoxic Folic Acid-Induced AKI.[J]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology:JASN,2017,28(1):218-29. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015121376.
[6] Ma DL,Li C,Jiang PL,et al. Inhibition of ferroptosis attenuates acute kidney injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Dig Dis Sci,2021,66(2):483-492. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-020-06225-2.
[7] Angeli JPF,Schneider M,Proneth B,et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice[J]. Nat Cell Biol,2014,16(12):1180-1191. DOI: 10.1038/ncb3064.
[8] Zhang J,Bi JB,Ren YF,et al. Involvement of GPX4 in irisin’s protection against ischemia reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury[J]. J Cell Physiol,2021,236(2):931-945. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.29903.
[9] Reznik E,Jiang H,Hakimi AA. Chemerin Tips the Scales in ccRCC to Evade Ferroptosis.[J]. Cancer discovery,2021,11(8):1879-80. DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.
[10] Grayson PC, Eddy S, Taroni JN, et al. Metabolic pathways and immunometabolism in rare kidney diseases[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2018: annrheumdis-2017. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212935.
[11] Brix SR,Stege G,Disteldorf E,et al. CC chemokine ligand 18 in ANCA-associated crescentic GN[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol,2015,26(9):2105-2117. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2014040407.
[12] Leek JT,Johnson WE,Parker HS,et al. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments[J]. Bioinformatics,2012,28(6):882-883. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts034.
[13] Wilkerson MD,Hayes DN. ConsensusClusterPlus: a class discovery tool with confidence assessments and item tracking[J]. Bioinformatics,2010,26(12):1572-1573. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq170.
[14] Lambrechts D,Wauters E,Boeckx B,et al. Phenotype molding of stromal cells in the lung tumor microenvironment[J]. Nat Med,2018,24(8):1277-1289. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0096-5.
[15] Friedman J,Hastie T,Tibshirani R. Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent[J]. J Stat Softw,2010,33(1):1-22.
[16] Sanz H,Valim C,Vegas E,et al. SVM-RFE: selection and visualization of the most relevant features through non-linear kernels[J]. BMC Bioinformatics,2018,19(1):432. DOI: 10.1186/s12859-018-2451-4.
[17] Shen SP,Wang GR,Zhang RY,et al. Development and validation of an immune gene-set based Prognostic signature in ovarian cancer[J]. EBioMedicine,2019,40:318-326. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.12.054.
[18] Zhang B,Wu Q,Li B,et al. m6A regulator-mediated methylation modification patterns and tumor microenvironment infiltration characterization in gastric cancer[J]. Mol Cancer,2020,19(1):53. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-020-01170-0.
[19] Jiang XJ,Stockwell BR,Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2021,22(4):266-282. DOI: 10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8.
[20] Law BMP,Wilkinson R,Wang XJ,et al. Interferon-γ production by tubulointerstitial human CD56bright natural killer cells contributes to renal fibrosis and chronic kidney disease progression[J]. Kidney Int,2017,92(1):79-88. DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.02.006.
[21] Berti A,Cavalli G,Campochiaro C,et al. Interleukin-6 in ANCA-associated vasculitis: rationale for successful treatment with tocilizumab[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum,2015,45(1):48-54. DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.02.002.
[22] Kallenberg CGM. Pathogenesis of ANCA-associated vasculitides[J]. Ann Rheum Dis,2011,70(Suppl 1):i59-i63. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.138024.
[23] Krolikoski M,Monslow J,Puré E. The CD44-HA axis and inflammation in atherosclerosis: a temporal perspective[J]. Matrix Biol,2019,78/79:201-218. DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.05.007.
[24] Kato T,Okumi M,Kakuta Y,et al. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells suppress acute cellular rejection via TSG-6 and CD44 interaction in rat kidney transplantation[J]. Transplantation,2014,98:336. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-201407151-01081.
[25] Kei U,Takashi M,Satoshi S,et al. Implantation of dedifferentiated fat cells ameliorated antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody glomerulonephritis by immunosuppression and increases in tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther,2022,13(1):319. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-03014-8.
[26] Justin K,Marsela B,Thomas BSI,et al. HSPB5 suppresses renal inflammation and protects lupus-prone NZB/W F1 mice from severe renal damage[J]. Arthritis Res Ther,2022,24(1):267. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-022-02958-9.
[27] Patino E, Bhatia D, Vance SZ, et al. Iron therapy mitigates chronic kidney disease progression by regulating intracellular iron status of kidney macrophages[J]. JCI Insight, 2023, 8(1). DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.159235.
[28] Motzer RJ,Banchereau R,Hamidi H,et al. Molecular subsets in renal cancer determine outcome to checkpoint and angiogenesis blockade[J]. Cancer Cell,2020,38(6):803-817.e4. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.10.011.
[29] Kuczler MD,Zieren RC,Dong L,et al. Advancements in the identification of EV derived mRNA biomarkers for liquid biopsy of clear cell renal cell carcinomas[J]. Urology,2022,160:87-93. DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2021.11.002.








 下载:
下载:


.png)